Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/EBLLandingpage: Difference between revisions
| Line 349: | Line 349: | ||
=== Discharge layer application === | === Discharge layer application === | ||
As exposure is done with an electron beam insulating substrates will cause a build up of charge that will deflect the incoming beam and disturb pattern definition. It is therefore necesarry When working with insulating substrates or substrates with thick (> 200 nm) dielectric films to apply a discharge layer. This is typically applied on top of the EBL resist layer and must be removed in between exposure and development. The most common discharge layer is 20 nm thermally evaporated Al. Bear in mind that it should be thermally evaporated and not e-beam evaporated. Thermal evaporation of Al can be done in [[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Thin film deposition/thermalevaporator|Thermal evaporator]] and [[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Thin film deposition//Wordentec|Wordentec]]. | As exposure is done with an electron beam insulating substrates will cause a build up of charge that will deflect the incoming beam and disturb pattern definition. It is therefore necesarry When working with insulating substrates or substrates with thick (> 200 nm) dielectric films to apply a discharge layer. This is typically applied on top of the EBL resist layer and must be removed in between exposure and development. The most common discharge layer is 20 nm thermally evaporated Al. Bear in mind that it should be thermally evaporated and not e-beam evaporated. Thermal evaporation of Al can be done in [[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Thin film deposition/thermalevaporator|Thermal evaporator]] and | ||
[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Thin film deposition//Wordentec|Wordentec]]. | |||
== Development == | == Development == | ||
Revision as of 09:32, 27 January 2023
Feedback to this page: click here
Electron-Beam Lithography at DTU Nanolab
DTU Nanolab has two EBL exposure systems, a JEOL JBX-9500FSZ and a Raith eLINE Plus system. The two systems are very different and new users should consult the EBL team to dertermine which system is appropriate for a particular project or type of sample. The general specifications of the two tools are given in the table below and may serve as a guideline for choice of system to use, especially the pros and cons list at the end of the table.
For more information and specific workflows on either tool, please refer to their respective pages; JEOL JBX-9500FSZ or Raith eLINE Plus.
Users can request training sessions on either of the two exposure systems by contacting e-beam@nanolab.dtu.dk. Please provide all relevant process information about your substrate/process in your inquiry.
| EBL system comparison table | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Equipment | JEOL JBX-9500FSZ | Raith eLINE Plus | |
| Performance | Resolution | 8 nm | 35 nm |
| Maximum writing field | 1mm x 1mm | 1mm x 1mm | |
| Process parameter range | Acceleration voltage | 100 kV | 1-30 kV |
| Scan speed | 100 MHz | 20 MHz | |
| Min. electron beam size | 4 nm | 10 nm | |
| Min. step size | 0.25 nm | 1 nm | |
| Beam current range | 0.1 nA to 100 nA | 0.01 to 12 nA | |
| Minimum dwell time | 10 ns | 50 ns | |
| Samples | Batch size |
Wafer cassettes:
|
|
| Substrate material allowed |
|
| |
| General considerations | Pros |
|
|
| Cons |
|
| |
Generalized workflow
While the EBL workflow resembles that of UV lithography there are a few additional complications and the parameter space is somewhat larger. The complications all arise from using electrons rather than light for exposure. Since a beam of electrons is used for exposure the substrate must be sufficiently conductive and grounded in order not to build up a charge. If the substrate in itself is not conductive a thin metal film or other conductive surface layer must be applied to it, read more on this in the resist section. Another complication is secondary exposure from backscattered electrons. This is a much bigger topic and covered in the pattern preparation section. A generalised workflow is shown below.
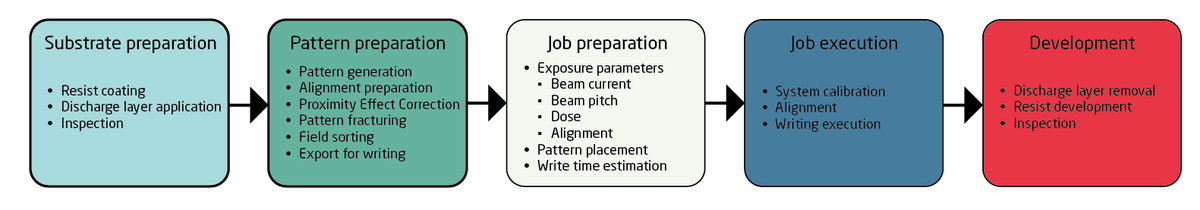
Since substrate preparation and development processes are (nearly) identical for the JEOL and Raith eLine systems they are described in common below. Pattern preparation, job preparation and job execution are fairly different between the two tools and hence these steps are described on the specific tool pages.
Substrate preparation
Resist coating
An appropriate EBL resist must naturally be applied to the substrate. DTU Nanolab supplies a number of standard resists, please consult the table below. The default positive EBL resist is AR-P 6200.09 (CSAR). CSAR installed on Spin Coater: Gamma E-beam and UV for spin coating of 2", 4" and 6" substrates. For other substrate sizes (i.e. chips) or other resists Spin Coater: LabSpin 02/03 have to be used instead. The standard resist bottles are stored in the chemical cupboard in E-4.
Contrary to most UV resist it is in general not advisable to use HMDS priming when coating with EBL resists. There can of course be exceptions to this but we do not recommend HMDS priming when using the DTU Nanolab supplied EBL resists.
| DTU Nanolab supplied standard EBL resists and process guides | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resist | Polarity | Manufacturer | Comments | Technical reports | Spin Coater | Thinner | Developer | Rinse | Remover | Process flows (in docx-format) |
| CSAR AR-P 6200 | Positive | AllResist | Standard positive resist, very similar to ZEP520. | AR-P 6200 info | Spin Coater: Gamma E-beam and UV or Spin Coater: LabSpin 02/03 | Anisole |
|
IPA |
|
CSAR CSAR with Al LOR5A with CSAR |
| Medusa AR-N 8200 | Negative | AllResist | Both e-beam and DUV sensitive resist. | AR-N 8200 info | Spin Coater: LabSpin 02/03 | AR 600-07 | AR 300-47:DIW (1:1) | DIW | BOE | |
| AR-N 7500 | Negative | AllResist | Both e-beam, DUV and UV-sensitive resist. | AR-N 7500 info | Spin Coater: LabSpin 02/03 | PGMEA |
|
DIW |
|
|
It is possible to obtain permission to user other resists at DTU Nanolab, users must however provide these resists and possibly developers themselves. A non-exhaustive list of user supplied EBL resist used at DTU Nanolab and some process guidelines can be found in the table below.
| Non standard, user supplied EBL resists and process guides | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resist | Polarity | Manufacturer | Comments | Technical reports | Spin Coater | Thinner | Developer | Rinse | Remover | Process flows (in docx-format) |
| ZEP520A | Positive resist, contact Lithography if you plan to use this resist | ZEON | Positive resist | ZEP520A.pdf, ZEP520A spin curves on SSE Spinner | See table here | Anisole | ZED-N50/Hexyl Acetate,n-amyl acetate, oxylene. JJAP-51-06FC05.pdf, JVB001037.pdf | IPA | acetone/1165 | Process_Flow_ZEP.docx
|
| Copolymer AR-P 617 | Positive | AllResist | Approved, not tested yet. Used for trilayer (PE-free) resist-stack or double-layer lift-off resist stack. Please contact Lithography for information. | AR_P617.pdf | See table here | PGME | AR 600-55, MIBK:IPA | acetone/1165 | Trilayer stack: Process_Flow_Trilayer_Ebeam_Resist.docx | |
| mr EBL 6000.1 | Negative | MicroResist | Standard negative resist | mrEBL6000 processing Guidelines.pdf | See table here | Anisole | mr DEV | IPA | mr REM | Process_Flow_mrEBL6000.docx |
| HSQ (XR-1541) | Negative | DOW Corning | Approved. Standard negative resist | HSQ Dow Corning, MSDS HSQ | See table here | TMAH, AZ400K:H2O | H2O | process flow HSQ | ||
| AR-N 7520 | Negative | AllResist | Both e-beam, DUV and UV-sensitive resist. Currently being tested, contact Peixiong Shi for information. | AR-N7500-7520.pdf | See table here | PGMEA | AR 300-47, TMAH | H2O | ||
| PMMA | Positive | AllResist | We have various types of PMMA in the cleanroom. Please contact Lithography for information. | See table here | Anisole | MIBK:IPA (1:3), IPA:H2O | IPA | acetone/1165/Pirahna |
| |
| ZEP7000 | Positive | ZEON | Not approved. Low dose to clear, can be used for trilayer (PEC-free) resist-stack. Please contact Lithography for information. | ZEP7000.pdf | See table here | Anisole | ZED-500/Hexyl Acetate,n-amyl acetate, oxylene. | IPA | acetone/1165 | Trilayer stack: Process_Flow_Trilayer_Ebeam_Resist.docx |
Discharge layer application
As exposure is done with an electron beam insulating substrates will cause a build up of charge that will deflect the incoming beam and disturb pattern definition. It is therefore necesarry When working with insulating substrates or substrates with thick (> 200 nm) dielectric films to apply a discharge layer. This is typically applied on top of the EBL resist layer and must be removed in between exposure and development. The most common discharge layer is 20 nm thermally evaporated Al. Bear in mind that it should be thermally evaporated and not e-beam evaporated. Thermal evaporation of Al can be done in Thermal evaporator and Wordentec.
Development
E-beam resists
Standard E-beam resists and process guidelines
DTU Nanolab offers a limited number of standard EBL resist for our users. Our standard resist and process guidelines are summarized below. CSAR (AR-P 6200.09) is installed on Spin coater Gamma E-beam & UV for easy spin coating of 2", 4" and 6" substrates. Other substrate sizes or resist have to be used in the Labspin 2/3 coating systems. The standard resist bottles are stored in the chemical cupboard in E-4.
| Resist | Polarity | Manufacturer | Comments | Technical reports | Spin Coater | Thinner | Developer | Rinse | Remover | Process flows (in docx-format) |
| CSAR AR-P 6200 | Positive | AllResist | Standard positive resist, very similar to ZEP520. | AR-P 6200 info | Gamma E-beam & UV or Labspin 2/3 | Anisole |
|
IPA |
|
Process Flow CSAR.docx Process Flow CSAR with ESPACER Process Flow CSAR with Al Process Flow LOR5A with CSAR |
| Medusa AR-N 8200 | Negative | AllResist | Both e-beam and DUV sensitive resist. | AR-N 8200 info | Labspin 2/3 | AR 600-07 | AR 300-47:DIW (1:1) | DIW | BOE | |
| AR-N 7500 | Negative | AllResist | Both e-beam, DUV and UV-sensitive resist. | AR-N 7500 info | Labspin 2/3 | PGMEA |
|
DIW |
|
Non-Standard E-beam resists
It is possible to obtain permission to user other resists at DTU Nanolab, users must however provide these resists and possibly developers themselves. A non-exhaustive list of user supplied EBL resist used at DTU Nanolab and some process guidelines can be found in the table below.
| Resist | Polarity | Manufacturer | Comments | Technical reports | Spin Coater | Thinner | Developer | Rinse | Remover | Process flows (in docx-format) |
| ZEP520A | Positive resist, contact Lithography if you plan to use this resist | ZEON | Positive resist | ZEP520A.pdf, ZEP520A spin curves on SSE Spinner | See table here | Anisole | ZED-N50/Hexyl Acetate,n-amyl acetate, oxylene. JJAP-51-06FC05.pdf, JVB001037.pdf | IPA | acetone/1165 | Process_Flow_ZEP.docx
|
| Copolymer AR-P 617 | Positive | AllResist | Approved, not tested yet. Used for trilayer (PE-free) resist-stack or double-layer lift-off resist stack. Please contact Lithography for information. | AR_P617.pdf | See table here | PGME | AR 600-55, MIBK:IPA | acetone/1165 | Trilayer stack: Process_Flow_Trilayer_Ebeam_Resist.docx | |
| mr EBL 6000.1 | Negative | MicroResist | Standard negative resist | mrEBL6000 processing Guidelines.pdf | See table here | Anisole | mr DEV | IPA | mr REM | Process_Flow_mrEBL6000.docx |
| HSQ (XR-1541) | Negative | DOW Corning | Approved. Standard negative resist | HSQ Dow Corning, MSDS HSQ | See table here | TMAH, AZ400K:H2O | H2O | process flow HSQ | ||
| AR-N 7520 | Negative | AllResist | Both e-beam, DUV and UV-sensitive resist. Currently being tested, contact Peixiong Shi for information. | AR-N7500-7520.pdf | See table here | PGMEA | AR 300-47, TMAH | H2O | ||
| PMMA | Positive | AllResist | We have various types of PMMA in the cleanroom. Please contact Lithography for information. | See table here | Anisole | MIBK:IPA (1:3), IPA:H2O | IPA | acetone/1165/Pirahna |
| |
| ZEP7000 | Positive | ZEON | Not approved. Low dose to clear, can be used for trilayer (PEC-free) resist-stack. Please contact Lithography for information. | ZEP7000.pdf | See table here | Anisole | ZED-500/Hexyl Acetate,n-amyl acetate, oxylene. | IPA | acetone/1165 | Trilayer stack: Process_Flow_Trilayer_Ebeam_Resist.docx |
User resist bottles in the cleanroom

We recommend all groups or users to have their own bottle of e-beam resist inside the cleanroom. Please follow the guidelines below.
- Find a blue-capped glass bottle in the cupboard next to office 055 in 346 (outside the cleanroom).
- Bring the bottle inside gowning; clean it thoroughly on the outside with water or alcohol
- Bring the bottle to a fumehood inside the cleanroom; clean the bottle and the lid thoroughly on the inside with the main solvent of your resist, i.e. for CSAR use anisole. If in doubt which solvent your e-beam resist contains, consult the MSDS of the resist found here.
- If you need to dilute the resist, find a measurement beaker and clean it thoroughly in same solvent as your own bottle. For CSAR, ZEP, mr EBL, and anisole-based PMMA, you can use the measurement beaker in the box inside the fumehood in E-4.
- Let the bottle dry in the fumehood.
- Bring the (main) bottle of resist to the fumehood. Carefully unscrew the lid of the resist bottle. If necessary, wipe the thread of the resist bottle before you pour resist into your own bottle; dried resists may sit on the thread and be transferred into your bottle (or worse into the large resist bottle) when pouring.
- Clean all bottles on the outside with acetone or IPA, let them fume off in the fumehood. Clean the measurement beaker as well.
- Find a label to your resist bottle; bottles without labels will be removed from the cleanroom.
- Write name, Lotnumber, group and date on your bottle.
When spin coating e-beam resist, you should use a pipette to transfer resist from your bottle to the substrate. If you pour the resist directly from your bottle, you will leave resist in the thread that will soon dry out and leave particles in the resist. The disposable pipettes need to be thoroughly cleaned with a N2 gun before use (app. 20 s). After some practice, you can obtain particle-free 4" wafers if bottle and pipette (and spin coater) are properly cleaned.
Keep your resist bottles in up-right position, do not tilt or shake them too much, this can spread particles from the sidewall into the resist.
Development
AR 600-546 and ZED N-50 developers are available in a semi automatic puddle developer Developer E-beam in E-4, mainly intended for development of AR-P 6200 and ZEP 520A. It has automatic recipes for puddle development cycles for 10, 30 and 60 seconds of either of the two developers, each finishing off with an IPA rinse and drying cycle. The system can handle chips, 2", 4" and 6" wafers.
Other resist have to be developed in the E-beam developer fumehood in E-4 in beakers. Please notice there are specific beaker sets for alkaline developers and for solvent based developers.
Proximity Error Correction (PEC)

Even though the electron beam diameter is only a few nm, the feature and pitch resolution in resist is limited by scattering of the electrons in the resist and substrate material. Forward scattering is scattering within the resist layer and it will have a broadening effect of the beam. The magnitude of this effect depends on acceleration voltage, resist composition and thickness of the resist layer. Back scattering is caused by electron-matter interaction in the substrate itself and electrons that are scattered back into the resist layer will provide a secondary (unwanted) exposure of the resist. The scattering distance is highly dependent on acceleration voltage and the substrate material. For a silicon substrate exposed at 100 kV the back scatter range is up to 30 µm and hence it is essential for many designs to account for this effect using PEC software. At DTU Nanolab we primarily use Beamer from GenISys for PEC. The PEC process will result in a dose modulated design file where the relative exposure dose has been modulated to ensure that all parts of the design receives a uniform dose regardless of whether a design feature is in a sparsely populated or a heavily populated area of the design.
For more information on PEC and use of Beamer please refer to our dedicated Beamer & PEC page.
Charging of non-conductive substrates
Exposure on a non-conducting substrate the accumulation of charges in the substrates will however destroy the e-beam patterning. To avoid this, a charge dissipating layer is added on top of the e-beam resist; this will provide a conducting layer for the electrons to escape, while high-energy electrons will pass through the layer to expose the resist.
At DTU Nanolab, we recommend to use a thin (20 nm) layer of thermally evaporated aluminum on top of the e-beam resist. Preferably, the thickness of Al and the e-beam dose should be optimised to the features you wish to e-beam pattern [1]. A good starting point is 20 nm Al; from here dose and development can be optimised to reach the resolution and feature size required. The aluminum layer is easily removed with MIF726 after exposure and prior to development of the e-beam resist.
The process flow for a standard e-beam exposure on CSAR with Al on top can be found here Process Flow CSAR with Al.
If your process can not utilize a aluminum discharge layer, Espacer might be another possibility to pursue. Espacer is a chemical that works as a discharging layer; it is spun onto the wafer on top of the resist and easily rinsed off the wafer after e-beam exposure. Visit this page for more information: Espacer
Literature on E-beam Lithography
- Lithography, Wiley, 2011: Chapter 3, Electron Beam Lithography by Stefan Landis: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/9781118557662.ch3/summary
