Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/UVLithography: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (167 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{cc-nanolab}} | |||
[ | '''Feedback to this page''': '''[mailto:labadviser@nanolab.dtu.dk?Subject=Feed%20back%20from%20page%20http://labadviser.nanolab.dtu.dk/index.php?title=Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/UVLithography click here]''' | ||
[[Category: Equipment|Lithography]] | |||
[[Category: Lithography]] | |||
[[Image:UVLithography.jpg|400px|right|]] | |||
__TOC__ | |||
=UV lithography= | |||
UV Lithography uses ultraviolet light to transfer a pattern from a photo-mask, or a digital design file, to a substrate coated with photoresist. | |||
The process has 3 main steps: | |||
# Coating the substrate with a photosensitive film | |||
# Transferring a pattern into the resist by exposing it with UV light through either a physical shadow mask or a digital version of a shadow mask | |||
# Developing the exposed resist to reveal the transferred pattern | |||
DTU Nanolab offers a number of automatic and manual coaters, mask or maskless exposure tools, as well as automatic or semi-automatic developers.<br clear=all /> | |||
= | =Getting started with UV lithography= | ||
[[File:UVLPic1.png|450px|right]] | |||
| | |||
[[File:UVLPic2.png|160px|right]] | |||
| | |||
<span style="color:red">New users are always recommended to have their process evaluated by the fabrication support group - before you start planning your UV process, and request training on UV lithography equipment, please go through the following pre-cleanroom and cleanroom steps and include all the information in your request.</span> | |||
Please remember that the [https://labadviser.nanolab.dtu.dk//index.php?title=Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography#Lithography_Tool_Package_Training Lithography TPT] is <i>mandatory</i> before you can receive training on any lithography equipment.<br> | |||
If you are completely new to photolithography, you can visit <u>[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Photolithography this]</u> wikipedia webpage about photolithography before you start. | |||
'''Pre-cleanroom work:''' | |||
# Complete the [https://labadviser.nanolab.dtu.dk//index.php?title=Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography#Lithography_Tool_Package_Training Lithography TPT] | |||
# Prepare a process flow: The process flow describes all steps in your UV lithography process. You can find docx-templates <u>[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/Resist/UVresist#UV_resist_comparison_table|in this table]]</u> | |||
# Evaluate your process in cooperation with the fabrication support group | |||
# Design device: Design your device and layout. A detailed instruction on how to design a layout (or mask) can be found <u>[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Pattern_Design|here]]</u> | |||
# Mask: If you wish to use a mask aligner, order a photomask for your UV process. Instructions on how to order a photomask can be found <u>[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Pattern_Design#Mask_Ordering_and_Fabrication|here]]</u> | |||
'''Cleanroom work:''' | |||
# Substrate pretreatment: In many processes it is recommended to <u>[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/Pretreatment|pre-treat or prime]]</u> your wafer before coating. In some <u>[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/Coaters|spin coaters]]</u>, these pre-treatment processes are included in the spin coating of resist | |||
# Resist Type: Choose the type of resist you wish to use: a list of UV lithography resist types available at DTU Nanolab can be found <u>[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/Resist#UV_Resist|on this page]]</u> | |||
#*Positive tone resist: Resist exposed to UV light will be dissolved in the developer. For mask aligners, the mask openings are an exact copy of the resist pattern which is to remain on the wafer | |||
#*Negative tone resist: Resist exposed to UV light will become polymerized and difficult to dissolve. For mask aligners, the mask openings are an ''inverse'' copy of the resist pattern which is to remain on the wafer | |||
# Thickness of resist: In general, it is recommended to work at, or below, an aspect ratio of ~1, i.e. where the feature sizes of the pattern, is larger than the thickness of the resist. Furthermore, when you decide on the resist thickness, consider which transfer method you need: | |||
#*For <u>[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/LiftOff|lift-off]]</u> processes, we recommend resist thickness at least 5 times larger than the thickness of the metal to be lifted | |||
#*For dry etch or wet etch processes, investigate the resist etch rate of your process, as this might limit the ''minimum'' thickness of your resist | |||
# Spin Coater: Do you need to use a manual spin coater or an automatic spin coater? See a list of spin coaters <u>[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/Coaters|here]]</u> | |||
# Exposure: Choose which aligner you wish to use, and consider the exposure dose | |||
#*You can find a list of mask aligners and maskless aligners <u>[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/UVExposure|here]]</u> | |||
#*You can find information on dose <u>[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/Resist#UV_Resist|here]]</u> | |||
# Development: Choose which equipment you wish to use to develop your photoresist from <u>[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/Development|this list]]</u>. Remember the development process influences the <u>[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/Resist#UV_Resist|exposure dose]]</u> | |||
# Specify whether you wish to strip or lift-off your resist: <u>[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/Strip|strip]]</u> and <u>[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/LiftOff|lift-off]]</u> | |||
<br clear=all /> | |||
<br clear= | |||
<!--- | |||
=Equipment and Process Pages= | |||
{{:Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/UVlithographyProcessPages}} | |||
===[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/Resist#UV_Resist|UV Resist]]=== | |||
===[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/Pretreatment|Pretreatment]]=== | ===[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/Pretreatment|Pretreatment]]=== | ||
===[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/Coaters|Coating]]=== | |||
===[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/Baking|Baking]]=== | ===[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/Baking|Baking]]=== | ||
===[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/UVExposure|UV Exposure Tools]]=== | |||
===[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/Development|Development]]=== | ===[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/Development|Development]]=== | ||
===[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/Descum|Descum]]=== | |||
===[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/ | |||
===[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/LiftOff|Lift-off]]=== | ===[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/LiftOff|Lift-off]]=== | ||
===[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/Strip|Stripping Resist]]=== | |||
---> | |||
== | =Process information from our suppliers= | ||
MicroChemicals GmbH has a [https://www.microchemicals.com/downloads/application_notes.html very large online library] of information about UV lithography. | |||
Of particular interest is the [https://www.microchemicals.com/dokumente/application_notes/lithography_trouble_shooting.pdf lithography trouble-shooter] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:51, 18 February 2026
The content on this page, including all images and pictures, was created by DTU Nanolab staff, unless otherwise stated.
Feedback to this page: click here

UV lithography
UV Lithography uses ultraviolet light to transfer a pattern from a photo-mask, or a digital design file, to a substrate coated with photoresist.
The process has 3 main steps:
- Coating the substrate with a photosensitive film
- Transferring a pattern into the resist by exposing it with UV light through either a physical shadow mask or a digital version of a shadow mask
- Developing the exposed resist to reveal the transferred pattern
DTU Nanolab offers a number of automatic and manual coaters, mask or maskless exposure tools, as well as automatic or semi-automatic developers.
Getting started with UV lithography
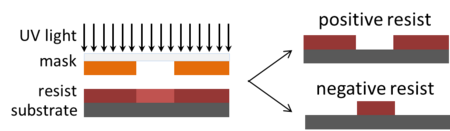
New users are always recommended to have their process evaluated by the fabrication support group - before you start planning your UV process, and request training on UV lithography equipment, please go through the following pre-cleanroom and cleanroom steps and include all the information in your request.
Please remember that the Lithography TPT is mandatory before you can receive training on any lithography equipment.
If you are completely new to photolithography, you can visit this wikipedia webpage about photolithography before you start.
Pre-cleanroom work:
- Complete the Lithography TPT
- Prepare a process flow: The process flow describes all steps in your UV lithography process. You can find docx-templates in this table
- Evaluate your process in cooperation with the fabrication support group
- Design device: Design your device and layout. A detailed instruction on how to design a layout (or mask) can be found here
- Mask: If you wish to use a mask aligner, order a photomask for your UV process. Instructions on how to order a photomask can be found here
Cleanroom work:
- Substrate pretreatment: In many processes it is recommended to pre-treat or prime your wafer before coating. In some spin coaters, these pre-treatment processes are included in the spin coating of resist
- Resist Type: Choose the type of resist you wish to use: a list of UV lithography resist types available at DTU Nanolab can be found on this page
- Positive tone resist: Resist exposed to UV light will be dissolved in the developer. For mask aligners, the mask openings are an exact copy of the resist pattern which is to remain on the wafer
- Negative tone resist: Resist exposed to UV light will become polymerized and difficult to dissolve. For mask aligners, the mask openings are an inverse copy of the resist pattern which is to remain on the wafer
- Thickness of resist: In general, it is recommended to work at, or below, an aspect ratio of ~1, i.e. where the feature sizes of the pattern, is larger than the thickness of the resist. Furthermore, when you decide on the resist thickness, consider which transfer method you need:
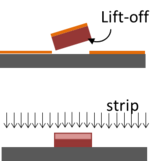
- For lift-off processes, we recommend resist thickness at least 5 times larger than the thickness of the metal to be lifted
- For dry etch or wet etch processes, investigate the resist etch rate of your process, as this might limit the minimum thickness of your resist
- Spin Coater: Do you need to use a manual spin coater or an automatic spin coater? See a list of spin coaters here
- Exposure: Choose which aligner you wish to use, and consider the exposure dose
- Development: Choose which equipment you wish to use to develop your photoresist from this list. Remember the development process influences the exposure dose
- Specify whether you wish to strip or lift-off your resist: strip and lift-off
Process information from our suppliers
MicroChemicals GmbH has a very large online library of information about UV lithography.
Of particular interest is the lithography trouble-shooter
