Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/EBLProcessExamples: Difference between revisions
Appearance
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
{| style="border: none; border-spacing: 0; margin: 1em auto; text-align: center;" | {| style="border: none; border-spacing: 0; margin: 1em auto; text-align: center;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[image:SingleShot1.png|400px]] || [[image:SingleShot2.png|400px]] || [[image: | | [[image:SingleShot1.png|400px]] || [[image:SingleShot2.png|400px]] || [[image:Singleshot3.png|400px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="3" style="text-align:center;| | | colspan="3" style="text-align:center;| | ||
Revision as of 11:49, 22 May 2024
This page is under construction. In time we will fill it with relevant process examples and relevant data.
Mix-and-match with EBL and UV lithography
Using mix-and-match it is possible to combine EBL and UV lithography using selected resists. Read more on the Mix-and-match page.
Single spot EBL on JEOL 9500
Arrays of circular holes can be created by normal area writing of a mask of circular structures. It can however also be done with a single spot approach, where the beam will dwell at each spot for several 100 ns and hence each spot will become a circular structure by local over exposure. You can read more about this method in the linked article.
Single-spot e-beam lithography for defining large arrays of nano-holes
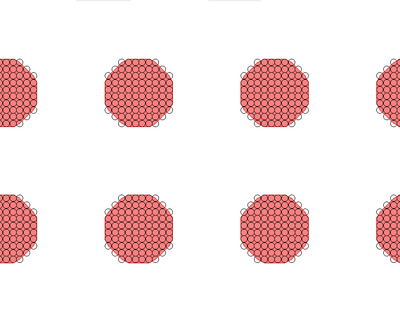 |
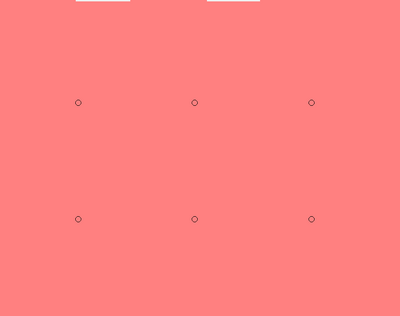 |
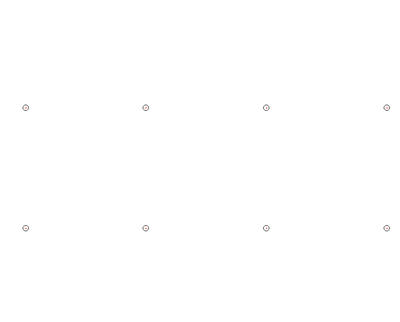
|
|
Bla | ||
Article on quality control on the JEOL 9500 system
Quality control of JEOL JBX-9500FSZ lithography system in a multi-user laboratory
