Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/EBLProcessExamples: Difference between revisions
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="3" style="text-align:center;| | | colspan="3" style="text-align:center;| | ||
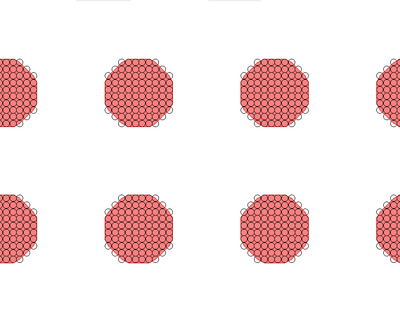
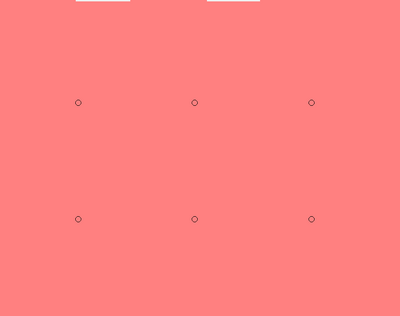
Example of the three different approaches for exposing arrays of circles. In all cases the red areas are the areas drawn in the mask file. The small circles indicate beam positions. | |||
|} | |} | ||
=Article on quality control on the JEOL 9500 system= | =Article on quality control on the JEOL 9500 system= | ||
''' [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167931716300466 Quality control of JEOL JBX-9500FSZ lithography system in a multi-user laboratory]''' | ''' [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167931716300466 Quality control of JEOL JBX-9500FSZ lithography system in a multi-user laboratory]''' | ||
Revision as of 11:53, 22 May 2024
This page is under construction. In time we will fill it with relevant process examples and relevant data.
Mix-and-match with EBL and UV lithography
Using mix-and-match it is possible to combine EBL and UV lithography using selected resists. Read more on the Mix-and-match page.
Single spot EBL on JEOL 9500
Arrays of circular holes can be created by normal area writing of a mask of circular structures. It can however also be done with a single spot approach, where the beam will dwell at each spot for several 100 ns and hence each spot will become a circular structure by local over exposure. You can read more about this method in the linked article.
Single-spot e-beam lithography for defining large arrays of nano-holes
 |
 |
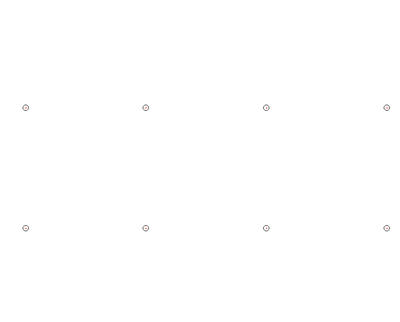
|
|
Example of the three different approaches for exposing arrays of circles. In all cases the red areas are the areas drawn in the mask file. The small circles indicate beam positions. | ||
Article on quality control on the JEOL 9500 system
Quality control of JEOL JBX-9500FSZ lithography system in a multi-user laboratory
