Specific Process Knowledge/Thermal Process/Resist Pyrolysis Furnace: Difference between revisions
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
!colspan="2" border="none" style="background:silver; color:black;" align="center"|Equipment | !colspan="2" border="none" style="background:silver; color:black;" align="center"|Equipment | ||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"|<b> | |style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"|<b>Reist Pyrolysis Furnace</b> | ||
|- | |- | ||
!style="background:silver; color:black;" align="center"|Purpose | !style="background:silver; color:black;" align="center"|Purpose | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
|style="background:LightGrey; color:black"|Process gasses | |style="background:LightGrey; color:black"|Process gasses | ||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"| | |style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"| | ||
* | *N<sub>2</sub> | ||
* | *H<sub>2</sub> | ||
* | *O<sub>2</sub> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:LightGrey; color:black"|Vacuum | |style="background:LightGrey; color:black"|Vacuum | ||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"| | |style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"| | ||
*Yes, but using | *Yes, but using N<sub>2</sub> and O<sub>2</sub> process gasses | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:LightGrey; color:black"|Nitrogen flows | |style="background:LightGrey; color:black"|Nitrogen flows | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
|style="background:LightGrey; color:black"|Batch size | |style="background:LightGrey; color:black"|Batch size | ||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"| | |style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"| | ||
* | *1-25 50 mm wafers (placed on a Si support wafers) | ||
* | *1-25 100 mm wafers | ||
* | *1-25 150 mm wafers | ||
*Several smaller samples if these are placed on a support wafer | *Several smaller samples if these are placed on a support wafer | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 11:04, 26 June 2017
Feedback to this page: click here
Resist Pyrolysis Furnace
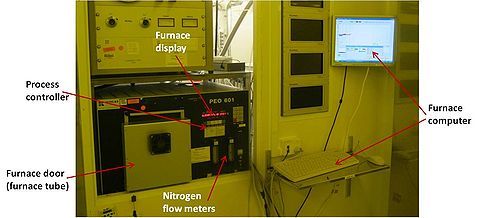
The Resist Pyrolysis Furnace is used for resist pyrolysis, where samples with different resist layers are heated up to maximum 1000 oC in a nitrogen atmosphere. At high temperatures carbon is formed by pyrolysis of the resist. In this way conductive structures can be made from a resist patterned sample.
If oxygen from the air or from outgassing of the resist is present in the furnace, the resist layer will be removed. Thus, for each process it is important to include a step with a high nitrogen flow at a lower temperature, before a high temperature for resist pyrolysis is obtained. Pyrolysis of a large amount of resist may also be a problem due to resist outgassing.
During processing the furnace is rapidly heated by use of six long heating lamps situated around the furnace tube, and cooling is done (rather slowly) by use of cooling fans. The furnace is purged with a controlable nitrogen flow. There is no vacuum on the furnace.
The user manual, user APV and contact information can be found in LabManager:
Process information
There are no standard processes on the furnace.
| Equipment | Reist Pyrolysis Furnace | |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose |
| |
| Process parameter range | Temperature |
|
| Process gasses |
| |
| Vacuum |
| |
| Nitrogen flows |
| |
| Substrates | Batch size |
|
| Allowed materials |
| |
