Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/LiftOff: Difference between revisions
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
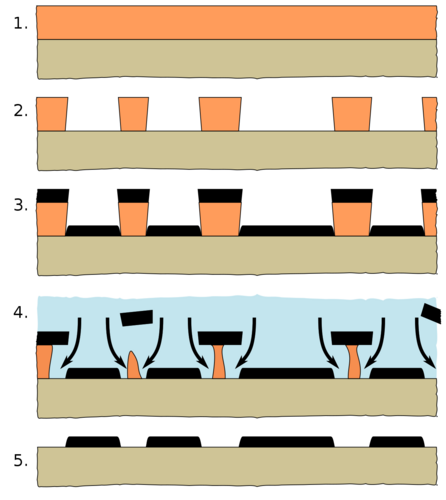
The image to the left shows a schematic of the lift off process. | The image to the left shows a schematic of the lift off process. | ||
*1. The substrate is coated with the masking material. | *'''1.''' The substrate is coated with the masking material. | ||
*2. The masking material is patterned. The mask must be a negative image of the desired material pattern. The mask sidewalls should be negative in order to prevent the material covering the sidewalls during deposition. | *'''2'''. The masking material is patterned. The mask must be a negative image of the desired material pattern. The mask sidewalls should be negative in order to prevent the material covering the sidewalls during deposition. | ||
*3. The material is deposited on top of both mask and substrate. | *'''3'''. The material is deposited on top of both mask and substrate. | ||
*4. The masking matreial is dissolved, thus lifting part of the deposited material. | *'''4'''. The masking matreial is dissolved, thus lifting part of the deposited material. | ||
*5. The remaining material forms the desired pattern on the substrate. | *'''5'''. The remaining material forms the desired pattern on the substrate. | ||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
Revision as of 10:29, 7 March 2014
THIS PAGE IS UNDER CONSTRUCTION
Feedback to this page: click here
Lift-off process
The lift-off process is used to pattern a material that can be deposited as a film on a substrate. The material is patterned by depositing the film on top of a patterned masking material, which is then dissolved, thus leaving only parts of the substrate covered in the material. Although this may in theory be done using any combination of mask and material, the most common is using photoresist as a lift-off mask for metal.
The image to the left shows a schematic of the lift off process.
- 1. The substrate is coated with the masking material.
- 2. The masking material is patterned. The mask must be a negative image of the desired material pattern. The mask sidewalls should be negative in order to prevent the material covering the sidewalls during deposition.
- 3. The material is deposited on top of both mask and substrate.
- 4. The masking matreial is dissolved, thus lifting part of the deposited material.
- 5. The remaining material forms the desired pattern on the substrate.
Comparing Lift-off equipment
| Equipment | Lift-off wet bench | Lift-off (4", 6") | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose |
|
| |
| Bath chemical |
Acetone |
NMP (Remover 1165) | |
| Process parameters | Process temperature |
Room temperature |
Heating of the bath is possible. The heating has been limited to 37°C |
| Ultrasonic agitation |
Continuous (on/off) |
Continuous or pulsed The power may be varied | |
| Substrates | Substrate size |
|
|
| Allowed materials |
Silicon or glass wafers Film or patterning of all but Type IV (Pb, Te) |
Silicon or glass wafers Film or patterning of all but Type IV (Pb, Te) | |
| Batch |
1 - 25 |
1 - 8 | |
Lift-off wet wench

This bench is only for wafers with metal!
The user manual, and contact information can be found in LabManager
Process information
Lift-off wet bench is used for lift-off using resists soluble in acetone. AZ 5214E is soluble in acetone, AZ nLOF is not.
Process recommandations for Lift-off wet bench:
- Place the wafers in a dedicated wafer holder.
- Put the holder in the acetone and start the ultrasound. The strip off time is depending of resist thickness.
- Rinse your wafers for 4-5 min. in running water after stripping.
For more information on image reversal of AZ 5214E, see here: Specific Process Knowledge/Photolithography/AZ5214E standard resist - reverse process
Lift-off (4", 6")

The user manual, and contact information can be found in LabManager
Process information
Lift-off (4", 6") is used for lift-off using resists that are soluble in NMP (N-Methyl-Pyrrolidone), supplied in the cleanroom as "Remover 1165". Both AZ 5214E and AZ nLOF are soluble in NMP.
