Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography: Difference between revisions
| (222 intermediate revisions by 10 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[ | '''Feedback to this page''': '''[mailto:labadviser@nanolab.dtu.dk?Subject=Feed%20back%20from%20page%20http://labadviser.nanolab.dtu.dk/index.php/Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography click here]''' | ||
Content and illustration by Thomas Pedersen, DTU Nanolab unless otherwise noted. | |||
[[Category: Equipment |Lithography exposure]] | |||
[[Category: Lithography|Exposure]] | |||
<div class="keywords" style="display:none;">ebl e-beam writer e-beamwriter ebeamwriter e-beamlithography</div> | |||
[[File:TPE02803.jpg|right|600px]] | |||
=Quick links= | |||
[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/JEOLRequest|Exposure slot request]] | |||
[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/JEOL 9500 User Guide|JEOL 9500 User Guide]] | |||
[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/FirstEBL|My first JEOL 9500 exposure tutorial]] | |||
[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/JEOLAlignment|Alignment exposure]] | |||
[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/Cassettes|JEOL cassette specifications]] | |||
[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/BEAMER|Beamer guide]] | |||
[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/TRACER|Tracer guide]] | |||
| | [[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/EBLProcessExamples|EBL process examples]] | ||
[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/Dose_Testing|Dose testing setups for JEOL 9500]] | |||
= Introduction to E-beam lithography at DTU Nanolab = | |||
DTU Nanolab has two E-beam writing systems, a JEOL JBX-9500 FSZ and a Raith eLINE Plus. The two systems are very different and new users should consult the EBL team to dertermine which system is appropriate for a particular project or type of sample. The general specifications of the two tools are given in the table below and may serve as a guideline for choice of system to use, especially the pros and cons list at the end of the table. Newcommers to EBL should start by watching our '''[https://youtu.be/2bFUO201DS4 JEOL 9500 process video]''' to see how a typical process is done. | |||
[[ | Compared to UV lithography EBL is somewhat more complicated and in general a significantly longer process. Writing time (per area) is much higher and thus EBL is only adviseable for structures with Critical Dimensions (CD) below 1 µm. For CD equal to or higher than 1 µm please consider our '''[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/UVExposure#Aligner:_Maskless_02 | Maskless Aligner tools.]]''' | ||
== Getting started and training in E-Beam Lithography == | |||
The JEOL 9500 system has a fairly steep learning curve and the information below and corresponding links are fairly comprehensive and describes uses and options that first time users of the JEOL 9500 system should not venture into. Instead, first time users of the JEOL 9500 system should consult our dedicated [[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/FirstEBL|My First JEOL 9500 Exposure guide]] which showcases a JEOL 9500 job from start to finish in a tutorial form. | |||
Please request training in E-Beam lithography by sending an email with your process flow to [mailto:training@nanolab.dtu.dk training@nanolab.dtu.dk]. | |||
==EBL staff at DTU Nanolab== | |||
Questions related to E-beam lithography should be directed to the EBL staff. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
|[[File:thope.png|150px]] || [[File:pxshi.png|150px]] || [[File:elelop.png|150px]] || [[File:meenadh.png|150px]] | |||
|- | |||
|[mailto:thope@dtu.dk Thomas Pedersen] | |||
JEOL 9500 & Raith E-Line | |||
|| [mailto:pxshi@dtu.dk Peixiong Shi] | |||
JEOL 9500 | |||
|| [mailto:elelop@dtu.dk Elena Lopez Aymerich] | |||
JEOL 9500 | |||
|| [mailto:meenadh@dtu.dk Meena Dhankhar] | |||
Raith E-Line | |||
|} | |||
== JEOL 9500 and Raith eLine Plus specifications == | |||
{| border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="10" width="60%" | |||
!colspan="4" border="none" style="background:silver; color:black;" align="center"|EBL system comparison table | |||
|- | |||
= | !colspan="2" border="none" style="background:silver; color:black;" align="center"|Equipment | ||
|style="background:silver; color:black;" align="left"|'''JEOL JBX-9500FSZ''' | |||
|style="background:silver; color:black;" align="left"|'''[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/eLINE|Raith eLINE Plus]]''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
!style="background:silver; color:black" align="left" valign="top" rowspan="2"|Performance | |||
|style="background:LightGrey; color:black"|Resolution | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"|8 nm | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"|35 nm | |||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:LightGrey; color:black"|Maximum writing field | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"|1mm x 1mm | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"|1mm x 1mm | |||
|- | |- | ||
!style="background:silver; color:black" align="left" valign="top" rowspan="6"|Process parameter range | |||
|style="background:LightGrey; color:black"|Acceleration voltage | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"|100 kV | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"|1-30 kV | |||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:LightGrey; color:black"|Scan speed | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"|200 MHz | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"|20 MHz | |||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:LightGrey; color:black"|Min. electron beam size | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"|4 nm | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"|10 nm | |||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:LightGrey; color:black"|Min. step size | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"|0.25 nm | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"|1 nm | |||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:LightGrey; color:black"|Beam current range | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"|0.1 nA to 100 nA | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"|0.01 to 12 nA | |||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:LightGrey; color:black"|Minimum dwell time | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"| 5 ns | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"| 50 ns | |||
|- | |- | ||
!style="background:silver; color:black" align="left" valign="top" rowspan="2"|Samples | |||
| | |style="background:LightGrey; color:black"|Batch size | ||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"| | |||
Wafer cassettes: | |||
*6 x 2" wafers | |||
*2 x 4" wafers | |||
*1 x 6" wafer | |||
*1 x 8" wafer | |||
*Special chip cassette with slit openings of 20 mm (position A), 12 mm (position B), 8 mm (position C) and 4 mm (position D). | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"| | |||
*Chips up to 75 x 75 mm | |||
*4" wafer holder | |||
*6" wafer holder (stage movement limited to central 100 x 100 mm region) | |||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:LightGrey; color:black"|Substrate material allowed | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"| | |||
*Silicon, quartz, pyrex, III-V materials | |||
*Wafers with layers of silicon oxide or silicon (oxy)nitride | |||
*Wafers with layers of metal | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"| | |||
*Silicon, quartz, pyrex, III-V materials | |||
*Wafers with layers of silicon oxide or silicon (oxy)nitride | |||
*Wafers with layers of metal | |||
|- | |- | ||
!style="background:silver; color:black" align="left" valign="top" rowspan="2"|General considerations | |||
|style="background:LightGrey; color:black"|Pros | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"| | |||
*100 kV | |||
*Sub 10 nm resolution | |||
*Automatic beam optimization | |||
*High current and process speed | |||
*Automatic sample exchange | |||
*High level of programmability for automatic job execution | |||
*EBL workhorse for large designs | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"| | |||
*Readily available | |||
*More intuitive software | |||
*Easier SEM mode alignment | |||
*Build in SEM automation for post exposure process control | |||
*2D stacks (HBN/graphene) allowed without Al coating | |||
*Excellent for small chips or small area design exposure | |||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:LightGrey; color:black"|Cons | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"| | |||
*Steep learning curve | |||
*Availability - booking calendar is usually full 5 weeks ahead | |||
|style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black"| | |||
*Maximum 30 kV | |||
*User dependent performance/beam optimization | |||
*Minimum feature size >35 nm | |||
*Difficult to handle design files >1 GB | |||
*Slower writing speed | |||
|} | |||
=Fundementals of EBL pattern writing= | |||
==Electron exposure== | |||
An E-beam writing system utilizes a focused electron beam to expose an electron sensitive resist in order to define a pattern on a substrate. For a positive tone resist the electron beam will scission polymer bonds within the resist to increase the dissolution rate when the substrate is placed in a developer solution. In this way the exposed part of the resist can be dissolved while maintaining the unexposed resist on the substrate. For a negative resist the electron beam will make the resist less soluble and hence the unexposed resist can be removed with a developer. | |||
{| style="border: none; border-spacing: 0; margin: 1em auto; text-align: center;" | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | [[image:PositiveNegative.png|700px]] | ||
|- | |||
| colspan="1" style="text-align:center;| | |||
Exposure and development result of a positive resist (left) and a negative resist (right). | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|} | |} | ||
In order to define a pattern in the resist enough electrons have to be supplied to the exposed area, i.e. the exposure dose has to be sufficiently high. The area exposure dose is expressed in units of µC/cm<sup>2</sup>. The dose to clear the resist (for a positive resist) can be obtained from a contrast curve such as the one below. Dose to clear varies a lot between different resist types and is also dependent on processing parameters such as | |||
< | |||
< | |||
*Acceleration voltage | |||
*Resist thickness | |||
*Developer agent and concentration | |||
*Post exposure baking | |||
In general it is always advisable to do a dose test of the pattern one intends to define to experimentally establish the optimum dose. For more information on resist dose please refer to the [[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/EBLsubstratePrep| EBL substrate preparation guide.]] | |||
{| | {| style="border: none; border-spacing: 0; margin: 1em auto; text-align: center;" | ||
|- | |||
| [[image:ContrastCurvesCSAR March2016 log.png|600px]] | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="1" style="text-align:center;| | |||
Contrast curve for AR-P 6200 exposed at 100 kV with the JEOL 9500 exposure system. Illustration: Tine Greibe. | |||
| | |||
| [[ | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|} | |} | ||
==Writing principle== | |||
Both of our EBL systems lets the user define a desired area dose to expose the resist with. Based on the beam current the systems will then calculate the necessary beam dwell to achieve the requested dose in the drawn areas. It is always the drawn (filled) parts of a pattern that will get exposed. In addition to area dose the Raith eLine tool allows the user to define a line dose for exposure of single lines. The JEOL 9500 system does not allow that. | |||
Before the pattern is exposed onto the substrate the pattern is broken down (fractured) into simple trapezoids and each trapezoidal shape is filled with beam shots, i.e. individual beam positions that together will make up the pattern. This is illustrated below with a simple pattern consisting of a square. The actual beam spot size is dependent on beam current and the pitch between beam positions is (within certain limitations) defined by the user. | |||
{| style="border: none; border-spacing: 0; margin: 1em auto; text-align: center;" | |||
|- | |||
| [[image:EBLBeamShots.png|200px]] | |||
|- | |||
{| | | colspan="1" style="text-align:center;| | ||
Simple shape filled in with beam shots. | |||
| | |||
| [[ | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|} | |} | ||
The electron source is continuously emitting electrons and exposure of the beam towards the sample is controlled by a beam blanker. The position of the beam is controlled by the beam deflector and scanning coils. The pattern is written one beam shot at a time in a serial process as this | |||
#Beam positioning for 1st beam position of current trapezoidal shape | |||
#Unblank the beam | |||
##Exposure | |||
##Reposition for next beam shot | |||
#Blank the beam at end of trapezoidal shape | |||
Steps 2.1 and 2.2 continues in a loop until all beam shots of the current trapezoidal shape has been executed after which the beam is blanked and the system moves on to the next trapezoidal shape. It is obvious that exposure in such a way is relatively slow and has an overhead on top of the actual exposure time since time is also spent on beam positioning and blanking/unblanking the beam. | |||
== | ==Exposure grid and exposure field== | ||
Both systems have a maximum writing field size of 1000 x 1000 µm<sup>2</sup> since the deflection of the beam is limited to ±500 µm in both x- and y-direction. Patterns inside a writing filed is written by beam deflection only and hence the substrate stage remains stationary. Geometry larger than a single writing field will be fractured across multiple writing fields and hence between fields the substrate stage will move to reposition the substrate directly under the column as illustrated below. | |||
{| style="border: none; border-spacing: 0; margin: 1em auto; text-align: center;" | |||
{| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| [[image:EBLFields.png|600px]] | |||
| | |- | ||
| colspan="1" style="text-align:center;| | |||
Illustration of a waveguide spanning four exposure fields. Between fields the stage will reposition the substrate below the column. | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|} | |} | ||
If neighbouring writing fields are not properly aligned features fractured across multiple writing fields may suffer from stitching errors, i.e. pattern discontinuities where the patterns do not align properly to each other. On the JEOL system write field alignment is ensured by a fully automated calibration sequence using internal alignment features. This ensures field stitching usually on the order of 10-15 nm or less. On the Raith system write field alignment is performed on the users own substrate and accuracy can vary. | |||
The beam shots described above are placed onto the systems exposure grid, hence the resolution of beam shot placement is governed by the exposure grid. The resolution of this grid is determined by the positioning DAC of the system, on the JEOL 9500 this is 20 bit and on the Raith eLine it is 16 bit. Hence the JEOL 9500 system has in principle 2<sup>20</sup> = 1.048.576 grid positions along each axis while the Raith system has 2<sup>16</sup> = 65.384 grid positions along each axis. This means the JEOL system can maintain a 1 nm exposure grid over the entire 1000 x 1000 µm<sup>2</sup> writing field whereas the Raith tool will have a 16 nm exposure grid at the maximum writing field. | |||
==Beam pitch, beam current and exposure dose relationship== | |||
A sample is exposed at a certain beam current. On the JEOL system this is selectable (in certain discrete steps) while on the Raith tool the beam current is bound by the choice of acceleration voltage and aperture. The user will input an area dose for the resist to be exposed with and the system will calculate the shot time (dwell time) of the beam to provide the requested dose. It is clear that high doses will require long dwell times whereas low doses will require short dwell times for the same beam current. There is however another important parameter to the dwell time calculation and that is the beam/shot pitch, i.e. how far beam shots are placed from each other. The beam scanner on the JEOL 9500 system is 100 MHz, thus the temporal resolution is 10 ns and it is not possible to have a beam shot (or dwell time) less than 10 ns. The Raith system has a 20 MHz beam scanner and hence the minimum shot time is 50 ns. This, in combination with beam current and exposure dose will set a lower limit on the beam pitch. | |||
The relation might not be obvious at first and is illustrated below. The two identical features are filled with beam shots at two different pitches. the right version has a lower beam pitch (half of the other) and thus there are simply many more beam shots. Consequently, to provide the same area exposure dose the shot time for the right side feature will be much shorter. At half the pitch there will be four times the number of beam shots and thus the shot time will be 1/4 the shot time of the left feature. | |||
== | {| style="border: none; border-spacing: 0; margin: 1em auto; text-align: center;" | ||
|- | |||
| [[image:BeamPitch.png|500px]] | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="1" style="text-align:center;| | |||
Example feature filled with beam shots at one times beam diameter (left) and half beam diameter (right). | |||
|} | |||
The shot time can be calculated as ''t = D·p<sup>2</sup>/I'', where ''D'' is the dose in µC/cm<sup>2</sup>, ''p'' is beam pitch and ''I'' is current. As a practical example let us consider an exposure at 2 nA beam current and a desired dose of 250 µC/cm<sup>2</sup>. At 4 nm beam pitch the shot time will come out to 20 ns, while at 2 nm beam pitch it will come out at 5 ns and thus violate the hardware limitation of 10 ns for the JEOL system. In order to expose the pattern with 2 nm shot pitch one would have to choose a lower beam current at the expense of increased writing time. | |||
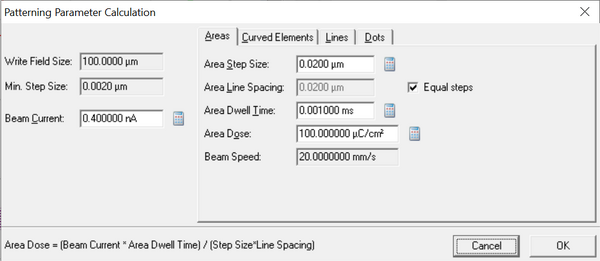
The shot time is in fact such an important number that both systems will tell the user what it is. On the JEOL system the shot time is displayed in a table after job compilation, see below. On the Raith tool it is indicated in the '''Patterning Parameter Calculation''' box, see below. | |||
{| style="border: none; border-spacing: 0; margin: 1em auto; text-align: center;" | |||
|- | |- | ||
|- | | <pre> | ||
Start estimation writing time ----- | |||
Shot counting start ----- | |||
thopeQU23008a.v30 at 11-MAR-2023 14:53:40 | |||
Shot counting end ----- | |||
Seq. writing time shottime[nsec] resist[uC/cm2] stdcur[nA] scanstep | |||
1 0:52:27 16.000 200.000 2.000 16 | |||
2 0:13:46 13.500 200.000 12.000 36 | |||
3 0:11:15 12.000 100.000 12.000 48 | |||
4 0:12:10 13.500 200.000 12.000 36 | |||
5 0:11:14 12.000 100.000 12.000 48 | |||
Total : 1:40:51 | |||
Estimation result file : thopeQU23008a.csv | |||
End estimation writing making time ----- | |||
</pre> || [[image:eLine_dose.PNG|600px]] | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="2" style="text-align:center;| | |||
Shot time as calculated by the JEOL system (left) and Raith eLine system (right). | |||
|} | |} | ||
==Exposure time== | |||
E-beam exposure is a serial writing process and the writing time (t) will scale with dose (D), area (A) and beam current (I) as: | |||
t = D*A/I | |||
It is thus essential to find the right balance between the area that needs to be defined and a beam current that will provide sufficient pattern fidelity and quality. During pattern writing the tool will also use time on cyclic calibration and stage movement as defined by the job path and pattern layout. The exposure time can be estimated based on the [[:File:Writing Time Estimator.xlsx|Writing Time Estimator Excel sheet]]. | |||
[[File: | |||
= Exposure information = | |||
== Generalized workflow == | |||
While the EBL workflow resembles that of UV lithography there are a few additional complications and the parameter space is somewhat larger. The complications all arise from using electrons rather than light for exposure. Since a beam of electrons is used for exposure the substrate must be sufficiently conductive and grounded in order not to build up a charge. If the substrate in itself is not conductive a thin metal film or other conductive surface layer must be applied to it, read more on this in the resist section. Another complication is secondary exposure from backscattered electrons. This is a much bigger topic and covered in the pattern preparation section. A generalised workflow is shown below. | |||
[[File:EBLWorkflow.png|1200px|frameless|center|alt=Generalized EBL workflow.|Generalized EBL workflow.]] | |||
Since substrate preparation and development processes are (nearly) identical for the JEOL and Raith eLine systems they are described in common below. Pattern preparation, job preparation and job execution are fairly different between the two tools and hence these steps are described on the specific tool pages. | |||
== | == Substrate preparation and resist information== | ||
Substrates must be prepared for EBL by applying an e-beam sensitive resist and possibly a discharge layer. Please consult the EBL substrate preparation guide on how to prepare your substrate and to find resist information. | |||
[[ | *[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/EBLsubstratePrep| EBL substrate preparation guide]] | ||
== Pattern preparation == | |||
Pattern preparation is somewhat different depending on if a pattern is exposed on JEOL 9500 or Raith eLine Plus. Please refer to the correct pattern preparation section below. | |||
[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/JEOLPatternPreparation|Pattern preparation for exposure on JEOL 9500.]] | |||
[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/RaithPatternPreparation|Pattern preparation for exposure on Raith eLine Plus.]] | |||
== Job preparation == | |||
Job preparation is also different depending on if a pattern is exposed on JEOL 9500 or Raith eLine Plus. Please refer to the correct job preparation section below. | |||
[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/JEOLJobPreparation|Job preparation for exposure on JEOL 9500.]] | |||
[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/RaithJobPreparation|Job preparation for exposure on Raith eLine Plus.]] | |||
== Job execution == | |||
Job execution is very different between the JEOL and Raith systems. The procedures are described on their respective user guide pages: | |||
*[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/JEOL 9500 User Guide|Job execution on JEOL 9500]] | |||
*[https://labmanager.dtu.dk/d4Show.php?id=18413&mach=445 Raith eLine Plus user manual] | |||
= | == Development == | ||
AR 600-546 and ZED N-50 developers are available in a semi automatic puddle developer [[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/Development#Developer:_E-beam|Developer: E-beam]] in E-4, mainly intended for development of AR-P 6200 and ZEP 520A. It has automatic recipes for puddle development cycles for 10, 30 and 60 seconds of either of the two developers, each finishing off with an IPA rinse and drying cycle. The system can handle chips, 2", 4" and 6" wafers. | |||
Other resist have to be developed in the E-beam developer fumehood in E-4 in beakers. Please notice there are specific beaker sets for alkaline developers and for solvent based developers. | |||
== | == Post development inspection == | ||
After development it is often necesarry to evaluate the result by SEM to verify feature dimensions. This can conviently be done in the Raith eLine Plus tool which apart from being an EBL tool is also a semiautomatic SEM. The strong suit of the tool is the ability to link/align a design file to the substrate and simply define image positions in the design file. The user can then set up a long list of image locations and the tool will acquire the SEM images without further user input. When set up correctly the system can acquire about one image per 5 seconds which is very advantageous for large arrays of structures. For an introduction to this, please refer to our [https://youtu.be/YoZF_6FeVb4 automatic SEM introduction video.] | |||
After image acquisition the images can be semi automatically processed with ProSEM to determine feature sizes. For large image sets the software can generate an Excel sheet with various dimension outputs. | |||
== | =EBL process examples= | ||
Process examples and results can be found [[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/EBLProcessExamples|on this page.]] | |||
= Literature on E-beam Lithography = | |||
* Handbook of Microlithography, Micromachining, and Microfabrication, Volume 1: Microlithography, P. Rai-Choudhury (Editor), chapter 2 (p 139 – 250). Link to book can be found here: http://www.cnf.cornell.edu/cnf_spietoc.html | |||
* Lithography, Wiley, 2011: Chapter 3, Electron Beam Lithography by Stefan Landis: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/9781118557662.ch3/summary | |||
Latest revision as of 12:47, 26 June 2024
Feedback to this page: click here
Content and illustration by Thomas Pedersen, DTU Nanolab unless otherwise noted.

Quick links
My first JEOL 9500 exposure tutorial
Dose testing setups for JEOL 9500
Introduction to E-beam lithography at DTU Nanolab
DTU Nanolab has two E-beam writing systems, a JEOL JBX-9500 FSZ and a Raith eLINE Plus. The two systems are very different and new users should consult the EBL team to dertermine which system is appropriate for a particular project or type of sample. The general specifications of the two tools are given in the table below and may serve as a guideline for choice of system to use, especially the pros and cons list at the end of the table. Newcommers to EBL should start by watching our JEOL 9500 process video to see how a typical process is done.
Compared to UV lithography EBL is somewhat more complicated and in general a significantly longer process. Writing time (per area) is much higher and thus EBL is only adviseable for structures with Critical Dimensions (CD) below 1 µm. For CD equal to or higher than 1 µm please consider our Maskless Aligner tools.
Getting started and training in E-Beam Lithography
The JEOL 9500 system has a fairly steep learning curve and the information below and corresponding links are fairly comprehensive and describes uses and options that first time users of the JEOL 9500 system should not venture into. Instead, first time users of the JEOL 9500 system should consult our dedicated My First JEOL 9500 Exposure guide which showcases a JEOL 9500 job from start to finish in a tutorial form.
Please request training in E-Beam lithography by sending an email with your process flow to training@nanolab.dtu.dk.
EBL staff at DTU Nanolab
Questions related to E-beam lithography should be directed to the EBL staff.
 |
 |
 |

|
| Thomas Pedersen
JEOL 9500 & Raith E-Line |
Peixiong Shi
JEOL 9500 |
Elena Lopez Aymerich
JEOL 9500 |
Meena Dhankhar
Raith E-Line |
JEOL 9500 and Raith eLine Plus specifications
| EBL system comparison table | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Equipment | JEOL JBX-9500FSZ | Raith eLINE Plus | |
| Performance | Resolution | 8 nm | 35 nm |
| Maximum writing field | 1mm x 1mm | 1mm x 1mm | |
| Process parameter range | Acceleration voltage | 100 kV | 1-30 kV |
| Scan speed | 200 MHz | 20 MHz | |
| Min. electron beam size | 4 nm | 10 nm | |
| Min. step size | 0.25 nm | 1 nm | |
| Beam current range | 0.1 nA to 100 nA | 0.01 to 12 nA | |
| Minimum dwell time | 5 ns | 50 ns | |
| Samples | Batch size |
Wafer cassettes:
|
|
| Substrate material allowed |
|
| |
| General considerations | Pros |
|
|
| Cons |
|
| |
Fundementals of EBL pattern writing
Electron exposure
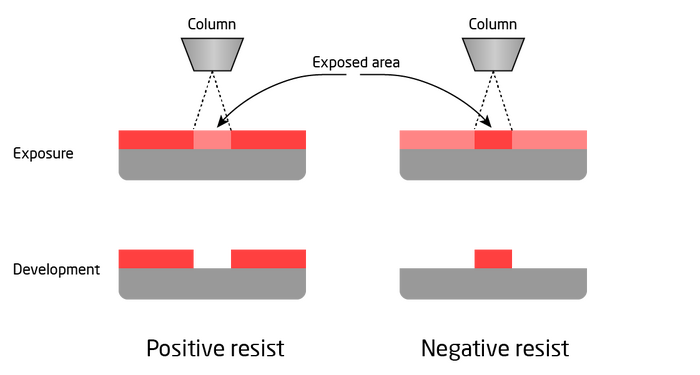
An E-beam writing system utilizes a focused electron beam to expose an electron sensitive resist in order to define a pattern on a substrate. For a positive tone resist the electron beam will scission polymer bonds within the resist to increase the dissolution rate when the substrate is placed in a developer solution. In this way the exposed part of the resist can be dissolved while maintaining the unexposed resist on the substrate. For a negative resist the electron beam will make the resist less soluble and hence the unexposed resist can be removed with a developer.
|
|
Exposure and development result of a positive resist (left) and a negative resist (right). |
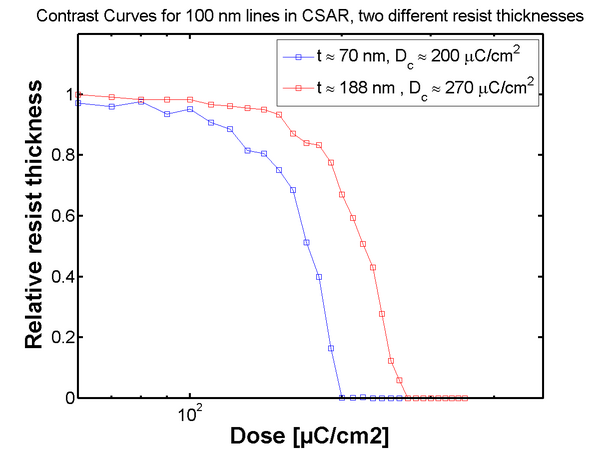
In order to define a pattern in the resist enough electrons have to be supplied to the exposed area, i.e. the exposure dose has to be sufficiently high. The area exposure dose is expressed in units of µC/cm2. The dose to clear the resist (for a positive resist) can be obtained from a contrast curve such as the one below. Dose to clear varies a lot between different resist types and is also dependent on processing parameters such as
- Acceleration voltage
- Resist thickness
- Developer agent and concentration
- Post exposure baking
In general it is always advisable to do a dose test of the pattern one intends to define to experimentally establish the optimum dose. For more information on resist dose please refer to the EBL substrate preparation guide.
|
|
Contrast curve for AR-P 6200 exposed at 100 kV with the JEOL 9500 exposure system. Illustration: Tine Greibe. |
Writing principle
Both of our EBL systems lets the user define a desired area dose to expose the resist with. Based on the beam current the systems will then calculate the necessary beam dwell to achieve the requested dose in the drawn areas. It is always the drawn (filled) parts of a pattern that will get exposed. In addition to area dose the Raith eLine tool allows the user to define a line dose for exposure of single lines. The JEOL 9500 system does not allow that.
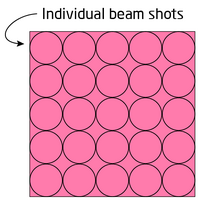
Before the pattern is exposed onto the substrate the pattern is broken down (fractured) into simple trapezoids and each trapezoidal shape is filled with beam shots, i.e. individual beam positions that together will make up the pattern. This is illustrated below with a simple pattern consisting of a square. The actual beam spot size is dependent on beam current and the pitch between beam positions is (within certain limitations) defined by the user.
|
|
Simple shape filled in with beam shots. |
The electron source is continuously emitting electrons and exposure of the beam towards the sample is controlled by a beam blanker. The position of the beam is controlled by the beam deflector and scanning coils. The pattern is written one beam shot at a time in a serial process as this
- Beam positioning for 1st beam position of current trapezoidal shape
- Unblank the beam
- Exposure
- Reposition for next beam shot
- Blank the beam at end of trapezoidal shape
Steps 2.1 and 2.2 continues in a loop until all beam shots of the current trapezoidal shape has been executed after which the beam is blanked and the system moves on to the next trapezoidal shape. It is obvious that exposure in such a way is relatively slow and has an overhead on top of the actual exposure time since time is also spent on beam positioning and blanking/unblanking the beam.
Exposure grid and exposure field
Both systems have a maximum writing field size of 1000 x 1000 µm2 since the deflection of the beam is limited to ±500 µm in both x- and y-direction. Patterns inside a writing filed is written by beam deflection only and hence the substrate stage remains stationary. Geometry larger than a single writing field will be fractured across multiple writing fields and hence between fields the substrate stage will move to reposition the substrate directly under the column as illustrated below.
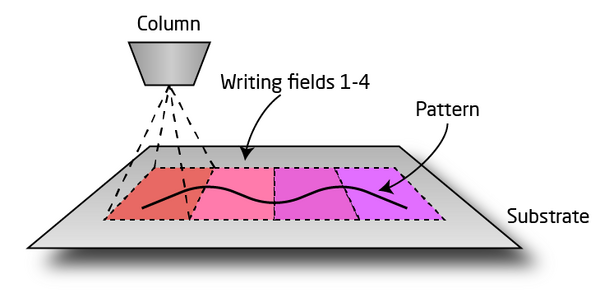
|
|
Illustration of a waveguide spanning four exposure fields. Between fields the stage will reposition the substrate below the column. |
If neighbouring writing fields are not properly aligned features fractured across multiple writing fields may suffer from stitching errors, i.e. pattern discontinuities where the patterns do not align properly to each other. On the JEOL system write field alignment is ensured by a fully automated calibration sequence using internal alignment features. This ensures field stitching usually on the order of 10-15 nm or less. On the Raith system write field alignment is performed on the users own substrate and accuracy can vary.
The beam shots described above are placed onto the systems exposure grid, hence the resolution of beam shot placement is governed by the exposure grid. The resolution of this grid is determined by the positioning DAC of the system, on the JEOL 9500 this is 20 bit and on the Raith eLine it is 16 bit. Hence the JEOL 9500 system has in principle 220 = 1.048.576 grid positions along each axis while the Raith system has 216 = 65.384 grid positions along each axis. This means the JEOL system can maintain a 1 nm exposure grid over the entire 1000 x 1000 µm2 writing field whereas the Raith tool will have a 16 nm exposure grid at the maximum writing field.
Beam pitch, beam current and exposure dose relationship
A sample is exposed at a certain beam current. On the JEOL system this is selectable (in certain discrete steps) while on the Raith tool the beam current is bound by the choice of acceleration voltage and aperture. The user will input an area dose for the resist to be exposed with and the system will calculate the shot time (dwell time) of the beam to provide the requested dose. It is clear that high doses will require long dwell times whereas low doses will require short dwell times for the same beam current. There is however another important parameter to the dwell time calculation and that is the beam/shot pitch, i.e. how far beam shots are placed from each other. The beam scanner on the JEOL 9500 system is 100 MHz, thus the temporal resolution is 10 ns and it is not possible to have a beam shot (or dwell time) less than 10 ns. The Raith system has a 20 MHz beam scanner and hence the minimum shot time is 50 ns. This, in combination with beam current and exposure dose will set a lower limit on the beam pitch.
The relation might not be obvious at first and is illustrated below. The two identical features are filled with beam shots at two different pitches. the right version has a lower beam pitch (half of the other) and thus there are simply many more beam shots. Consequently, to provide the same area exposure dose the shot time for the right side feature will be much shorter. At half the pitch there will be four times the number of beam shots and thus the shot time will be 1/4 the shot time of the left feature.
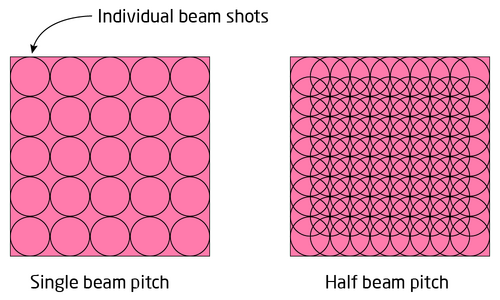
|
|
Example feature filled with beam shots at one times beam diameter (left) and half beam diameter (right). |
The shot time can be calculated as t = D·p2/I, where D is the dose in µC/cm2, p is beam pitch and I is current. As a practical example let us consider an exposure at 2 nA beam current and a desired dose of 250 µC/cm2. At 4 nm beam pitch the shot time will come out to 20 ns, while at 2 nm beam pitch it will come out at 5 ns and thus violate the hardware limitation of 10 ns for the JEOL system. In order to expose the pattern with 2 nm shot pitch one would have to choose a lower beam current at the expense of increased writing time.
The shot time is in fact such an important number that both systems will tell the user what it is. On the JEOL system the shot time is displayed in a table after job compilation, see below. On the Raith tool it is indicated in the Patterning Parameter Calculation box, see below.
Exposure time
E-beam exposure is a serial writing process and the writing time (t) will scale with dose (D), area (A) and beam current (I) as: t = D*A/I
It is thus essential to find the right balance between the area that needs to be defined and a beam current that will provide sufficient pattern fidelity and quality. During pattern writing the tool will also use time on cyclic calibration and stage movement as defined by the job path and pattern layout. The exposure time can be estimated based on the Writing Time Estimator Excel sheet.
Exposure information
Generalized workflow
While the EBL workflow resembles that of UV lithography there are a few additional complications and the parameter space is somewhat larger. The complications all arise from using electrons rather than light for exposure. Since a beam of electrons is used for exposure the substrate must be sufficiently conductive and grounded in order not to build up a charge. If the substrate in itself is not conductive a thin metal film or other conductive surface layer must be applied to it, read more on this in the resist section. Another complication is secondary exposure from backscattered electrons. This is a much bigger topic and covered in the pattern preparation section. A generalised workflow is shown below.
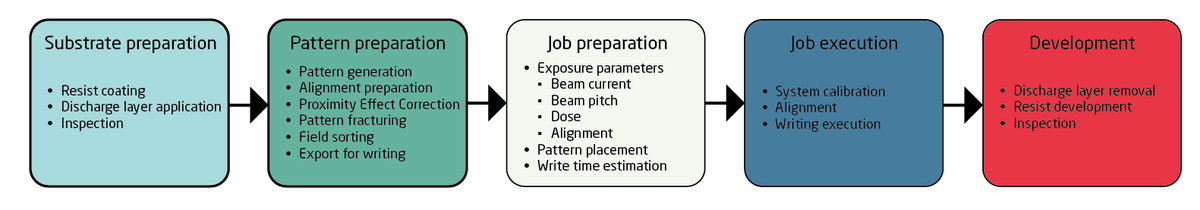
Since substrate preparation and development processes are (nearly) identical for the JEOL and Raith eLine systems they are described in common below. Pattern preparation, job preparation and job execution are fairly different between the two tools and hence these steps are described on the specific tool pages.
Substrate preparation and resist information
Substrates must be prepared for EBL by applying an e-beam sensitive resist and possibly a discharge layer. Please consult the EBL substrate preparation guide on how to prepare your substrate and to find resist information.
Pattern preparation
Pattern preparation is somewhat different depending on if a pattern is exposed on JEOL 9500 or Raith eLine Plus. Please refer to the correct pattern preparation section below.
Pattern preparation for exposure on JEOL 9500.
Pattern preparation for exposure on Raith eLine Plus.
Job preparation
Job preparation is also different depending on if a pattern is exposed on JEOL 9500 or Raith eLine Plus. Please refer to the correct job preparation section below.
Job preparation for exposure on JEOL 9500.
Job preparation for exposure on Raith eLine Plus.
Job execution
Job execution is very different between the JEOL and Raith systems. The procedures are described on their respective user guide pages:
Development
AR 600-546 and ZED N-50 developers are available in a semi automatic puddle developer Developer: E-beam in E-4, mainly intended for development of AR-P 6200 and ZEP 520A. It has automatic recipes for puddle development cycles for 10, 30 and 60 seconds of either of the two developers, each finishing off with an IPA rinse and drying cycle. The system can handle chips, 2", 4" and 6" wafers.
Other resist have to be developed in the E-beam developer fumehood in E-4 in beakers. Please notice there are specific beaker sets for alkaline developers and for solvent based developers.
Post development inspection
After development it is often necesarry to evaluate the result by SEM to verify feature dimensions. This can conviently be done in the Raith eLine Plus tool which apart from being an EBL tool is also a semiautomatic SEM. The strong suit of the tool is the ability to link/align a design file to the substrate and simply define image positions in the design file. The user can then set up a long list of image locations and the tool will acquire the SEM images without further user input. When set up correctly the system can acquire about one image per 5 seconds which is very advantageous for large arrays of structures. For an introduction to this, please refer to our automatic SEM introduction video.
After image acquisition the images can be semi automatically processed with ProSEM to determine feature sizes. For large image sets the software can generate an Excel sheet with various dimension outputs.
EBL process examples
Process examples and results can be found on this page.
Literature on E-beam Lithography
- Handbook of Microlithography, Micromachining, and Microfabrication, Volume 1: Microlithography, P. Rai-Choudhury (Editor), chapter 2 (p 139 – 250). Link to book can be found here: http://www.cnf.cornell.edu/cnf_spietoc.html
- Lithography, Wiley, 2011: Chapter 3, Electron Beam Lithography by Stefan Landis: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/9781118557662.ch3/summary