Specific Process Knowledge/Characterization/Element analysis
You can make detailed analysis on the elemental composition and distribution in a sample with 3 instruments at Danchip. The Leo SEM and FEI SEM are both equipped with an X-ray detector that allows you to make elemental analysis by using the technique Energy Dispersive X-ray analysis or EDX. The Atomika SIMS uses a technique called Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry or SIMS.
Energy Dispersive X-ray analysis
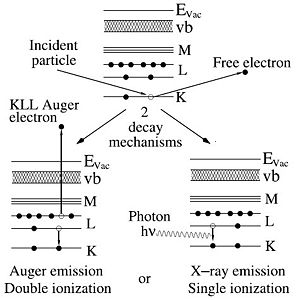
The technique of extracting information from the X-rays generated in a sample that is irradiated with electrons is called energy dispersive X-ray analysis or EDX. (Other acronyms are Energy Dispersive x-ray Spectroscopy, EDS, or Electron Probe Microanalysis, EPMA). The energetic electrons in the incident beam create core level vacancies as they collide with sample atoms electrons in a multiple scattering process. This leaves the atoms in the sample in an excited state. In the process of decaying from this state photons may be emitted. The energy of these photons is determined by the difference in energy of the shells involved. Since atomic shells are unique for every element so will be the transitions between them. Thus, every element has its own characteristic X-ray spectrum that can be used to determine the elemental composition.
Adding an EDX detector to a SEM provides a very powerful tool for elemental analysis. The capability of the SEM to precisely maneuver the electron beam in a number of ways enables us to make point-like analysis with nanometer precision.
Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry
When a solid sample is sputtered by primary ions of few keV energy, a fraction of the particles emitted from the target is ionized. Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry consists of analyzing these secondary ions with a mass spectrometer. Secondary ion emission by a solid surface under ion bombardment supplies information about the elemental, isotopic and molecular composition of its uppermost atomic layers.
| SEM with EDX | SIMS | |
|---|---|---|
| Full name | Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis | Secondary Ion Mass Spectroscopy |
| Technique | Non destructive method: X-rays are generated when the primary beam impinge on the sample. The elemental analysis is possible because the energy of these photons is characteristic of the element they emitted from. | Destructive method: A beam of high energy heavy ions (caesium or oxygen) sputters off surface atoms that are subsequently measured with a mass spectrometer. |
| What elements are detected | Every element heavier than boron/carbon | Every element |
| Chemical information | None: Only transistions involving inner shell electrons are detected | None |
| Sample limitations | Vacuum compatible. | Vacuum compatible. The sample needs to be cut into small pieces. |
| Spatial resolution | Very precise point-like analysis is possible with SEM electron beam. | Limited to what is visible in a camera |
| Depth resolution | The size interaction volume depends on the SEM high voltage and sample density: The higher the SEM high voltage the bigger and deeper the interaction volume. The more dense the material is the smaller is the interaction volume. | The sputtering of the surface makes it possible to perform detailed depth profiling with extremely good sensitivity and depth resolution. |
| Detection limit | Approximately 1 % atomic | Down to 1 ppb for many elements |
