Specific Process Knowledge/Thermal Process/Oxidation: Difference between revisions
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
| | | | ||
! | ! | ||
[http://labadviser.danchip.dtu.dk/index.php/Specific_Process_Knowledge/Thermal_Process/A1_Bor_Drive-in_furnace|A1: Boron Drive-in] | [http://labadviser.danchip.dtu.dk/index.php/Specific_Process_Knowledge/Thermal_Process/A1_Bor_Drive-in_furnace| A1: Boron Drive-in] | ||
! | ! | ||
[http://labadviser.danchip.dtu.dk/index.php/Specific_Process_Knowledge/Thermal_Process/C2_Gate_Oxide_furnace| A2: Gate Oxide] | [http://labadviser.danchip.dtu.dk/index.php/Specific_Process_Knowledge/Thermal_Process/C2_Gate_Oxide_furnace| A2: Gate Oxide] | ||
Revision as of 14:31, 10 March 2014
Feedback to this page: click here
Oxidation
At Danchip we have seven furnaces for oxidation: A1, A2, A3, C1, C3, D1 and Nobel. Oxidation can take place either by a dry process or a wet process. The film quality of dry oxide is better than for wet oxide with regards to density and dielectric constant. If the film quality for the wet oxide is acceptable then the thickness and the time it takes to grow the oxide often decides if a dry or wet oxidation is chosen.
- Dry oxidation is used from 5 nm - 200 nm. Can be grown in furnaces: A1, A2, A3, C1, C3.
- Wet oxidation is used up to 4 µm can be grown in furnace: A1, A3, Nobel.
- Very thick oxide >4 µm can be grown in D1, it is still a wet oxidation.
The standard recipes, quality control limits and results for the Boron Drive-in and Phosphorus Drive-in furnaces can be found here:
- Standard recipes, QC limits and results for the Boron Drive-in + Predep furnace (A1)
- Standard recipes, QC limits and results for the Phosphorus Drive-in furnace (A3)
Comparison of the seven oxidation furnaces
| Generel description | Drive-in of boron deposited in the boron pre-dep furnace(A1) or drive-in of ion implanted boron. Can also be used for dry and wet oxidation. | Oxidation of gate-oxide and other especially clean oxides. | Drive-in of phosphorous deposited in the phosphorous pre-dep furnace(A4) or drive-in of ion implanted phosphorous. Can also be used for dry and wet oxidation. | Oxidation and annealing of 6" wafers. Oxidation of new wafer with out RCA cleaning. Annealing of wafers from the LPCVD furnaces and PECVD1. | Oxidation and annealing of wafers from EVG-NIL, PECVD3 and wafers with aluminum. | Oxidation of very thick oxides, thickness higher than 4 µm. | Oxidation and annealing of almost materials on silicon wafer. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxidation method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Annealing gas |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Process temperatur |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Substrate and Batch size |
Including one test wafer |
Including one test wafer |
Including one test wafer |
Including one test wafer |
Including one test wafer |
|
|
| Allowed materials |
All wafers have to be RCA cleaned. Except for Boron pre-dep wafer from furnace A1. |
All wafers have to be RCA cleaned. |
All wafers have to be RCA cleaned. Except for Phosphorous pre-dep wafers from furnace A4. |
All processed wafers have to be RCA cleaned. Except for wafers from LPCVD furnace and PECVD1. |
All wafers have to be RCA cleaned. Except for wafers from EVG-NIL, PECVD3 and wafer for annealing of aluminum. |
Only new wafers |
Almost all meterials |
Oxidation curves
Generic calculator for wet/dry oxide thickness calculation
The following links give an approximate oxide time/thickness based on a general formula.
Wet Oxidation on <100>
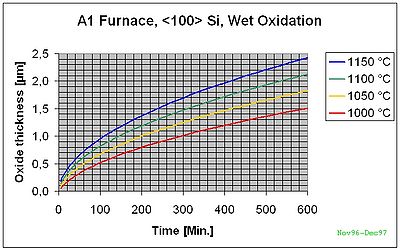
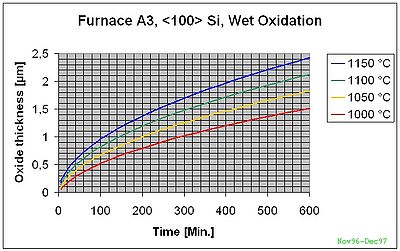
The curves below are based on measurements in our specific furnaces and give more accurate results.
- Wet oxidation
-
A1 Furnace <100>-Si Wet Oxidation
-
A3 Furnace <100>-Si Wet Oxidation
Dry Oxidation on <100> and <111> wafer
- Dry oxidation
-
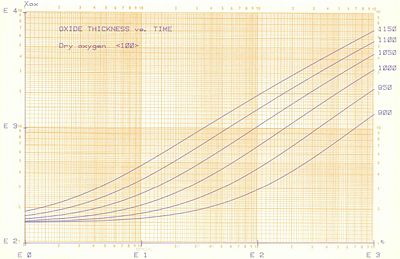
Dry oxide on <100> wafer. The y-axis is in Å and the x-axis is in minutes.
-
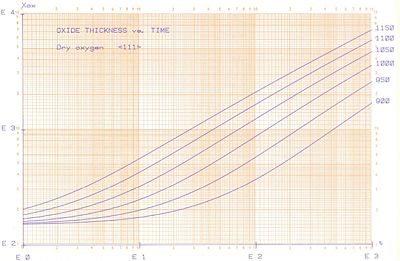
Dry oxide on <111> wafer. The y-axis is in Å and the x-axis is in minutes.