Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/Pretreatment: Difference between revisions
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==Comparing pretreatment methods== | ==Comparing pretreatment methods== | ||
{|border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="3" style="text-align:left;" | |||
|- | |||
|- | |||
|-style="background:silver; color:black" | |||
! | |||
![[Specific Process Knowledge/Etch/Wet Silicon Oxide Etch (BHF)|Wet Silicon Oxide etch (BHF/HF)]] | |||
![[Specific Process Knowledge/Etch/RIE (Reactive Ion Etch)|RIE (Reactive Ion Etch)]] | |||
![[Specific Process Knowledge/Etch/AOE (Advanced Oxide Etch)|AOE (Advanced Oxide Etch)]] | |||
![[Specific Process Knowledge/Etch/IBE⁄IBSD Ionfab 300|IBE/IBSD Ionfab 300]] | |||
|- | |||
|- | |||
|-style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black" | |||
!Generel description | |||
| | |||
*Isotropic etch | |||
| | |||
*Anisotropic etch: vertical sidewalls | |||
| | |||
*Anisotropic etch: vertical sidewalls | |||
| | |||
*Primarily for pure physical etch by sputtering with Ar-ions | |||
|- | |||
|- | |||
|-style="background:LightGrey; color:black" | |||
!Possible masking materials | |||
| | |||
*Photoresist | |||
*PolySilicon | |||
*Silicon nitride (LPCVD) | |||
*Blue film | |||
*Cr/Au for deeper etches (plastic beaker) | |||
| | |||
*Photoresist | |||
*DUV resist | |||
*E-beam resist | |||
*Silicon Oxide | |||
*Silicon Nitride | |||
*Metals if they cover less than 5% of the wafer area (ONLY RIE2!) | |||
| | |||
*Photoresist | |||
*DUV resist | |||
*E-beam resist | |||
*Silicon Oxide | |||
*Silicon Nitride | |||
*Aluminium | |||
*Chromium (Please try to avoid this) | |||
| | |||
*Any material that is accepted in the machine | |||
|- | |||
|- | |||
|-style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black" | |||
!Etch rate range | |||
| | |||
*~75 nm/min (Thermal oxide) in BHF | |||
*~90 nm/min (Thermal oxide) in SIO Etch | |||
*~25 nm/min (Thermal oxide) in 5%HF | |||
*~3-4µm/min in 40%HF | |||
| | |||
*Process dependent | |||
*Tested range: ~20nm/min - ~120nm/min | |||
| | |||
*Process dependent | |||
*Tested range: ~230nm/min - ~550nm/min | |||
| | |||
*Process dependent | |||
*Tested once ~22nm/min | |||
|- | |||
|- | |||
|-style="background:LightGrey; color:black" | |||
!Substrate size | |||
| | |||
*<nowiki>#</nowiki>1-25 100mm wafers in our 100mm bath | |||
*What can be fitted in a plastic beaker | |||
| | |||
*As many small samples as can be fitted on the 100mm carrier. | |||
*<nowiki>#</nowiki>1 100mm wafer (or smaller with carrier) | |||
*<nowiki>#</nowiki>1 150mm wafer (only RIE2 when set up for 150mm) | |||
| | |||
*As many small samples as can be fitted on a 100mm wafer | |||
*<nowiki>#</nowiki>1 50 mm wafer fitted on a 100mm wafer | |||
*<nowiki>#</nowiki>1 100 mm wafer | |||
*<nowiki>#</nowiki>1 150 mm wafers (only when the system is set up to 150mm) | |||
| | |||
*As many samples as can be securely fitted on a up to 200mm wafer | |||
*<nowiki>#</nowiki>1 50 mm wafer with special carrier | |||
*<nowiki>#</nowiki>1 100 mm wafer with special carrier | |||
*<nowiki>#</nowiki>1 150 mm wafers with special carrier | |||
*<nowiki>#</nowiki>1 200 mm wafer | |||
|- | |||
|-style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black" | |||
!Allowed materials | |||
| | |||
In the dedicated bath: | |||
*Silicon | |||
*Silicon Oxide | |||
*Silicon Nitride | |||
*Silicon Oxynitride | |||
*Photoresist | |||
*Blue film | |||
In a plastic beaker: | |||
*No limits cross contamination wise | |||
| | |||
*Silicon | |||
*Silicon Oxide | |||
*Silicon Nitride | |||
*Silicon Oxynitride | |||
*Photoresist | |||
*DUV resist | |||
*E-beam resist | |||
*Other metals if they cover less than 5% of the wafer area (ONLY RIE2!) | |||
*Quartz/fused silica | |||
| | |||
*Silicon | |||
*Silicon Oxide | |||
*Silicon Nitride | |||
*Silicon Oxynitride | |||
*Photoresist | |||
*DUV resist | |||
*E-beam resist | |||
*Aluminium | |||
*Chromium (try to avoid it) | |||
*Quartz/fused silica | |||
| | |||
*Silicon | |||
*Silicon oxides | |||
*Silicon (oxy)nitrides | |||
*Metals from the +list | |||
*Metals from the -list | |||
*Alloys from the above list | |||
*Stainless steel | |||
*Glass | |||
*III-V materials | |||
*Resists | |||
*Polymers | |||
*Capton tape | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
<br clear="all" /> | |||
=HMDS= | =HMDS= | ||
Revision as of 14:52, 7 February 2014
Feedback to this page: click here
Pretreatment
All surfaces can be divided to hydrophilic or hydrophobic surfaces, where the oxidized surfaces such SiO2 or surface with native oxide formation on Si or Al substrates consider to be hydrophilic and have very bad wetting with hydrophobic resist.
Therefore it is very important to do the pretreatment step before the spinning. Here we will give an overview of treatments available at Danchip to promote photoresist adhesion.
Comparing pretreatment methods
| Wet Silicon Oxide etch (BHF/HF) | RIE (Reactive Ion Etch) | AOE (Advanced Oxide Etch) | IBE/IBSD Ionfab 300 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Generel description |
|
|
|
|
| Possible masking materials |
|
|
|
|
| Etch rate range |
|
|
|
|
| Substrate size |
|
|
|
|
| Allowed materials |
In the dedicated bath:
In a plastic beaker:
|
|
|
|
HMDS
Feedback to this section: click here
The chemical treatment with hexamethyldisilazane (HMDS) before the spin coating can be used to promote the adhesion for photoresist. HMDS treatment leaves a mono-layer of TMS (trimethylsilyl) on the Si or SiO2 surface.
The molecular formula for hexamethyldisilazane, or bis(trimethylsilyl)amine, is C6H19NSi2. Here is a schematic overview of HMDS treatment of silicon-oxide surface.
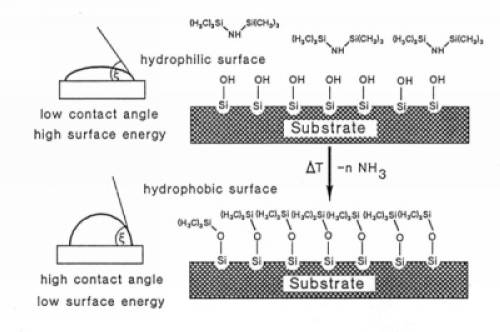
Comparing HMDS priming
| Equipment | HMDS oven | Spin Track 1 + 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose |
|
| |
| Priming chemical |
hexamethyldisilizane (HMDS) | ||
| Performance | Contact angle |
standard recipe 82° (on SiO2) |
60° - 90°; standard recipe 82° (on SiO2) |
| Process parameters | Process temperature |
150°C |
50°C |
| Process time |
32.5 minutes |
3 min / wafer | |
| Substrates | Substrate size |
|
100 mm wafers |
| Allowed materials |
All cleanroom materials |
Silicon (with oxide, nitride, or metal films or patterning) Glass (borosilicate and quartz) | |
| Batch |
1 - 25, multiple batches possible |
1 - 25 | |
HMDS oven

At Danchip we use Star2000 model from IMTEC to do vapor deposition of hexamethyldisilizane (HMDS) under the special conditions: low pressure and high chamber temperature. The result of the dehydration bake and HMDS prime is that the wafers become hydrophobic after the treatment.
The user manual, user APV, and contact information can be found in LabManager:
Process information
- Recipe 4: baseline prime process with 5 min priming time
Baseline prime process description:
1. Vacuum, 2 min
2. Nitrogen pump, 3.5 min
3. Heat- up, 10 min
4. Vacuum, 4.5 min
5. HMDS prime, 5 min
6. Vacuum chamber exhaust, 3 min
7. Nitrogen back-fill, 3.5 min
| Purpose |
Promotion of photoresist adhesion by hydrophobization | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical |
hexamethyldisilizane | ||
| Performance | Contact angle |
82° (on SiO2) | |
| Process parameters | Process temperature |
150 °C | |
| Process time |
32.5 minutes | ||
| Substrates | Substrate size |
| |
| Allowed materials |
All cleanroom materials | ||
| Batch |
1 - 25, multiple batches possible | ||
Buffered HF-Clean

Another commonly used method to render the surface of silicon wafers hydrophobic is the dilute HF dip.
BHF is mostly used to do pretreatment step for new Si wafers. The native dioxide layer will be removed during 30 sec etching and in this way we will promote the resist adhesion on the Si substrates. We recommend to spin resist asap after the procedure.
Oven 250C

The oven is typically used for pretreatment (dehydration) of Si and glass substrates to promote the resist adhesion. We recommend to place the wafers in metal carrier in the oven at least for 4 hours, better during the night, and spin the resist on them asap.
