Specific Process Knowledge/Characterization/PL mapper: Difference between revisions
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{cc-nanolab}} | |||
'''Feedback to this page''': '''[mailto:labadviser@Nanolab.dtu.dk?Subject=Feed%20back%20from%20page%20http://labadviser.Nanolab.dtu.dk/index.php?title=Specific_Process_Knowledge/characterisation/PL_Mapper click here]''' | '''Feedback to this page''': '''[mailto:labadviser@Nanolab.dtu.dk?Subject=Feed%20back%20from%20page%20http://labadviser.Nanolab.dtu.dk/index.php?title=Specific_Process_Knowledge/characterisation/PL_Mapper click here]''' | ||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
==PhotoLuminescence Mapper RPM2000 == | ==PhotoLuminescence Mapper RPM2000 == | ||
[[Image:PL-mapper.jpg|500px|right|thumb|Positioned in the MOCVD room: F-1, {{photo1}}]] | [[Image:PL-mapper.jpg|500px|right|thumb|Positioned in the MOCVD room: F-1, {{photo1}}]] | ||
Photoluminescence mapping is a non-contact, non-destructive technique for mapping out uniformity of alloy composition, material quality and defects in substrates and of III-V epiwafers. The Rapid Photoluminiscence Mapper (RPM) is equipped with 3 lasers for PL measurements and a white-light source to map out thickness and reflectance of eg layers, microcavities and VCSELs. | Photoluminescence mapping is a non-contact, non-destructive technique for mapping out uniformity of alloy composition, material quality and defects in substrates and of III-V epiwafers. The Rapid Photoluminiscence Mapper (RPM) is equipped with 3 lasers for PL measurements and a white-light source to map out thickness and reflectance of eg layers, microcavities and VCSELs. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 13: | ||
It can also be used to map out voids after silicon wafer-bonding. This is done using the reflectance mapping and is using the fact that silicon is transparent for wavelengths above ~1000nm. A void will therefor change the reflectance in that wavelength range. See datasheet below (Thanks to Jens Hemmingsen for the data). | It can also be used to map out voids after silicon wafer-bonding. This is done using the reflectance mapping and is using the fact that silicon is transparent for wavelengths above ~1000nm. A void will therefor change the reflectance in that wavelength range. See datasheet below (Thanks to Jens Hemmingsen for the data). | ||
The user manual and contact information can be found in [http://www.labmanager.dtu.dk/function.php?module=Machine&view=view&mach=152 '''LabManager''']. | |||
[http://www.labmanager.dtu.dk/function.php?module=Machine&view=view&mach=152 | |||
{| border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="10" | {| border="2" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="10" | ||
Latest revision as of 18:44, 27 May 2025
The content on this page, including all images and pictures, was created by DTU Nanolab staff, unless otherwise stated.
Feedback to this page: click here
PhotoLuminescence Mapper RPM2000

Photoluminescence mapping is a non-contact, non-destructive technique for mapping out uniformity of alloy composition, material quality and defects in substrates and of III-V epiwafers. The Rapid Photoluminiscence Mapper (RPM) is equipped with 3 lasers for PL measurements and a white-light source to map out thickness and reflectance of eg layers, microcavities and VCSELs.
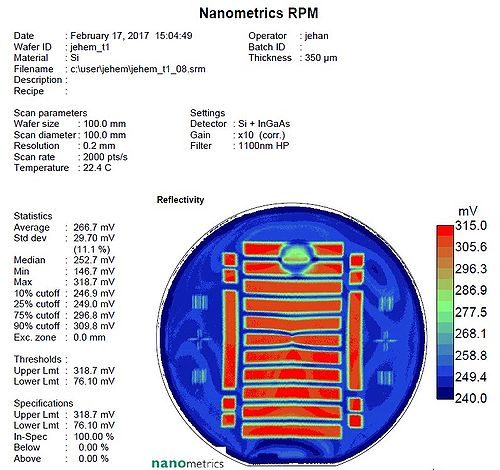
It can also be used to map out voids after silicon wafer-bonding. This is done using the reflectance mapping and is using the fact that silicon is transparent for wavelengths above ~1000nm. A void will therefor change the reflectance in that wavelength range. See datasheet below (Thanks to Jens Hemmingsen for the data).
The user manual and contact information can be found in LabManager.
| Performance | Excitation |
|
|---|---|---|
| Detection |
| |
| Gratings |
| |
| Chuck sizes |
| |
| Resolution |
| |
| Wavelength accuracy |
| |
| Materials | Allowed substrate materials |
|
| Forbidden materials |
| |
| Software | RPM viewer |
|
