Specific Process Knowledge/Thermal Process/Oxidation: Difference between revisions
| (33 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Feedback to this page''': '''[mailto:thinfilm@ | '''Feedback to this page''': '''[mailto:thinfilm@nanolab.dtu.dk?Subject=Feed%20back%20from%20page%20http://labadviser.danchip.dtu.dk/index.php/Specific_Process_Knowledge/Thermal_Process/Oxidation) click here]''' | ||
<i> Unless otherwise stated, this page is written by <b>DTU Nanolab internal</b></i> | |||
==Oxidation== | ==Oxidation== | ||
At DTU Nanolab we have | At DTU Nanolab we have eight furnaces and one RTP (rapid thermal processors) which can be used for thermal oxidation of silicon samples: Boron Drive-in and Pre-dep furnace (A1), Gate Oxide furnace (A2), Phosphorus Drive-in furnace (A3), Anneal-oxide furnace (C1), Anneal-Bond furnace (C3), Al-Anneal furnace (C4), Oxidation 8" furnace (E1), Resist Pyrolysis furnace and RTP Annealsys. | ||
Thermal oxidation can take place either by a dry process or by a wet process, depending on what furnace that is used for the oxidation. The film quality for a dry oxide is better than the film quality for a wet oxide with regards to density and dielectric constant. However, the oxidation rate is slowest for dry oxidation. | |||
*Dry oxidation is used to grow 5 nm - 300 nm of silicon oxide. Dry oxidation can be done in the A1, A2, A3, C1, C3, C4, E1 and Resist Pyrolysis furnaces. | |||
*Wet oxidation is used to grow up to ~3 µm of silicon oxide. Wet oxidation can be done in the A1, A3, C1, C3 and E1 furnaces. | |||
Wafers with oxide layers thicker than ~3 µm can normally not be made in the cleanroom and will have to be bought from somewhere else (but check the wafer shop first - there might be some on stock). It is NOT allowed to oxidize the same wafers two times to get a thicker layer than 3 µm without approval. | |||
Thermal oxidation can done at temperatures up to 1050 C - 1150 C, depending on the furnace - and especially the diameter of the quartz tube in the furnace. At these high temperatures, the quartz tube might start to deform, so therefore the oxidation times are restricted: | |||
*Maximum allowed oxidation time at 1150 C: 8 hours | *A1, A2, A3, C3 and C4 furnaces: Maximum allowed oxidation time at 1150 C: 8 hours | ||
*Maximum allowed oxidation time at 1100 C: 23 hours (this will result in ~3 um wet oxide) | *A1, A2, A3, C1, C3, C4 and E1 furnaces: Maximum allowed oxidation time at 1100 C: 23 hours (this will result in ~3 um wet oxide) | ||
*Resist Pyrolysis furnace: Maximum allowed oxidation time at 1050 C: 3 hours | |||
The standard recipes, quality control limits and results for the Boron Drive-in + Pre-dep furnace (A1) and the Phosphorus Drive-in furnace (A3) can be found here: | The standard recipes, quality control limits and results for the Boron Drive-in + Pre-dep furnace (A1) and the Phosphorus Drive-in furnace (A3) can be found here: | ||
*[[Specific Process Knowledge/Thermal Process/A1 Bor Drive-in furnace|Standard recipes, QC limits and results for the Boron Drive-in + Predep furnace (A1)]] | |||
*[[Specific Process Knowledge/Thermal Process/A1 | |||
*[[Specific Process Knowledge/Thermal Process/A3 Phosphor Drive-in furnace|Standard recipes, QC limits and results for the Phosphorus Drive-in furnace (A3)]] | *[[Specific Process Knowledge/Thermal Process/A3 Phosphor Drive-in furnace|Standard recipes, QC limits and results for the Phosphorus Drive-in furnace (A3)]] | ||
| Line 36: | Line 35: | ||
*[[Specific Process Knowledge/Thermal Process/Oxidation/Standard oxidation recipes]] | *[[Specific Process Knowledge/Thermal Process/Oxidation/Standard oxidation recipes]] | ||
==Comparison of the | ==Comparison of the oxidation furnaces== | ||
{|border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding=" | {|border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="9" style="text-align:left;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 46: | Line 45: | ||
| | | | ||
! | ! | ||
[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Thermal_Process/A1_Bor_Drive-in_furnace|Boron Drive-in | [[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Thermal_Process/A1_Bor_Drive-in_furnace|Boron Drive-in and Pre-dep furnace (A1)]] | ||
! | ! | ||
[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Thermal_Process/A2_Gate_Oxide_furnace|Gate Oxide furnace (A2)]] | [[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Thermal_Process/A2_Gate_Oxide_furnace|Gate Oxide furnace (A2)]] | ||
| Line 56: | Line 55: | ||
[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Thermal_Process/C3_Anneal-bond_furnace|Anneal Bond furnace (C3)]] | [[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Thermal_Process/C3_Anneal-bond_furnace|Anneal Bond furnace (C3)]] | ||
! | ! | ||
[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Thermal_Process/ | [[Specific Process Knowledge/Thermal Process/C4 Aluminium Anneal furnace|Al-Anneal furnace (C4)]] | ||
! | |||
[[Specific Process Knowledge/Thermal Process/E1 Furnace Oxidation (8")|Oxidation 8" furnace (E1)]] | |||
! | |||
[[Specific Process Knowledge/Thermal Process/Resist Pyrolysis furnace|Resist Pyrolysis furnace (research tool)]] | |||
! | |||
[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Thermal_Process/RTP Annealsys| RTP Annealsys (research tool)]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 62: | Line 67: | ||
|-style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black" | |-style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black" | ||
!Generel description | !Generel description | ||
|Dry and wet oxidation | | | ||
|Dry oxidation of gate | *Dry and wet oxidation | ||
|Dry and wet oxidation | *Boron pre-deposition and boron drive-in are also done in the furnace | ||
|Dry and wet oxidation of 100 mm and 150 mm wafers | | | ||
|Dry and wet oxidation and annealing of wafers from | *Dry oxidation of e.g. gate oxides layers | ||
|Dry oxidation and annealing of | | | ||
*Dry and wet oxidation | |||
*Phosphorous drive-in is also done in the furnace | |||
| | |||
*Dry and wet oxidation of 100 mm and 150 mm wafers | |||
*Oxidation and annealing of wafers from the LPCVD furnaces and PECVD4 | |||
| | |||
*Dry and wet oxidation and annealing of wafers from the wafer bonders and from PECVD4 and PECVD3 | |||
| | |||
*Dry oxidation of 100 mm wafers and small samples | |||
| | |||
*Dry and wet oxidation of 150 mm and 200 mm wafers | |||
| | |||
*Dry oxidation of silicon and annealing in N<sub>2</sub>. But the furnace is mainly being used for pyrolysis of different resists | |||
| | |||
*Rapid thermal processing: | |||
**RTA (annealing) | |||
**RTO (oxidation) | |||
**RTN (nitridation) | |||
**RTH (hydrogenation) | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 75: | Line 99: | ||
| | | | ||
*Dry: O<sub>2</sub> | *Dry: O<sub>2</sub> | ||
*Wet: | *Wet: H<sub>2</sub>O (torch) | ||
| | |||
*Dry: O<sub>2</sub> | |||
| | |||
*Dry: O<sub>2</sub> | |||
*Wet: H<sub>2</sub>O (torch) | |||
| | |||
*Dry: O<sub>2</sub> | |||
*Wet: H<sub>2</sub>O (steamer) | |||
| | | | ||
*Dry: O<sub>2</sub> | *Dry: O<sub>2</sub> | ||
*Wet: H<sub>2</sub>O (bubbler) | |||
| | | | ||
*Dry: O<sub>2</sub> | *Dry: O<sub>2</sub> | ||
| | | | ||
*Dry: O<sub>2</sub> | *Dry: O<sub>2</sub> | ||
*Wet: | *Wet: H<sub>2</sub>O (steamer) | ||
| | | | ||
*Dry: O<sub>2</sub> | *Dry: O<sub>2</sub> | ||
| | | | ||
*Dry: O<sub>2</sub> | *Dry: O<sub>2</sub> | ||
| Line 106: | Line 137: | ||
| | | | ||
*N<sub>2</sub> | *N<sub>2</sub> | ||
*H<sub>2</sub> | | | ||
*N<sub>2</sub> | |||
| | |||
*N<sub>2</sub> | |||
| | |||
*Ar | |||
*5% H<sub>2</sub>/Ar | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 113: | Line 150: | ||
!Process temperature | !Process temperature | ||
| | | | ||
* | *800 <sup>o</sup>C - 1150 <sup>o</sup>C | ||
| | |||
*800 <sup>o</sup>C - 1150 <sup>o</sup>C | |||
| | |||
*800 <sup>o</sup>C - 1150 <sup>o</sup>C | |||
| | |||
*800 <sup>o</sup>C - 1100 <sup>o</sup>C | |||
| | | | ||
* | *800 <sup>o</sup>C - 1150 <sup>o</sup>C | ||
| | | | ||
* | *400 <sup>o</sup>C - 1150 <sup>o</sup>C | ||
| | | | ||
* | *800 <sup>o</sup>C - 1100 <sup>o</sup>C | ||
| | | | ||
* | *25 <sup>o</sup>C - 1050 <sup>o</sup>C | ||
| | | | ||
* | *700 <sup>o</sup>C - 1200 <sup>o</sup>C | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 140: | Line 182: | ||
*1-30 100 mm wafers | *1-30 100 mm wafers | ||
| | | | ||
*1-30 50 mm wafers | *1-30 50 mm wafers | ||
*1-30 100 mm wafers | *1-30 100 mm wafers | ||
*1-30 150 mm wafers | *1-30 150 mm wafers | ||
| | | | ||
*1-30 50 mm wafers | |||
*1-30 100 mm wafers | |||
*Small samples on a carrier wafer, horizontal | *Small samples on a carrier wafer, horizontal | ||
| | |||
*1-30 50 mm wafers | *1-30 50 mm wafers | ||
*1-30 100 mm wafers | *1-30 100 mm wafers | ||
*1-2 150 mm wafers, horizontal, less good uniformity | |||
*Small samples on a carrier wafer, horizontal | |||
| | | | ||
*1- | *1-50 150 mm wafers | ||
*1-50 200 mm wafers | *1-50 200 mm wafers | ||
*Small samples on a carrier | | | ||
|- | *1-30 50 mm wafers | ||
*1-30 100 mm wafers | |||
*1-30 150 mm wafers | |||
*Small samples on a carrier wafers, horizontal | |||
| | |||
*Single-wafer process | |||
*Chips on carrier | |||
*100 mm or 150 mm wafers | |||
|- | |- | ||
|-style="background:LightGrey; color:black" | |-style="background:LightGrey; color:black" | ||
!'''Allowed materials''' | !'''Allowed materials''' | ||
| | | | ||
*All wafers have to be RCA cleaned, except boron pre-doped wafers from the same furnace | *All wafers have to be RCA cleaned, except boron pre-doped wafers from the same furnace | ||
| | | | ||
*All wafers have to be RCA cleaned | *All wafers have to be RCA cleaned | ||
| | | | ||
*All wafers have to be RCA cleaned, except phosphorous pre-doped wafers from furnace A4 | *All wafers have to be RCA cleaned, except phosphorous pre-doped wafers from furnace A4 | ||
| | | | ||
*All processed wafers have to be RCA cleaned, except wafers from LPCVD furnaces and PECVD4 | *All processed wafers have to be RCA cleaned, except wafers from LPCVD furnaces and PECVD4 | ||
| | | | ||
*All processed wafers have to be RCA cleaned, except for wafers from | *All processed wafers and samples have to be RCA cleaned, except for wafers from the wafers bonders and from PECVD4 and PECVD3 | ||
| | | | ||
* | *No RCA cleaning required | ||
** | | | ||
** | *All processed wafers have to be RCA cleaned. | ||
| | |||
*Only samples for resist pyrolysis, and all sample materials have to be approved by DTU Nanolab. Samples with metals and III-V materials are NOT allowed | |||
| | |||
*Silicon | |||
*Silicon Nitride | |||
*Aluminum Oxide | |||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 374: | Line 432: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==Breakdown voltage measurements== | |||
In order to evaluate the quality of the oxide layers that can be grown in the oxidation furnaces, some breakdown voltage measurement have been made. | |||
The results can be found on this page: | |||
*[[Specific Process Knowledge/Thermal Process/Oxidation/Breakdown voltage measurements]] | *[[Specific Process Knowledge/Thermal Process/Oxidation/Breakdown voltage measurements]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:40, 16 September 2025
Feedback to this page: click here
Unless otherwise stated, this page is written by DTU Nanolab internal
Oxidation
At DTU Nanolab we have eight furnaces and one RTP (rapid thermal processors) which can be used for thermal oxidation of silicon samples: Boron Drive-in and Pre-dep furnace (A1), Gate Oxide furnace (A2), Phosphorus Drive-in furnace (A3), Anneal-oxide furnace (C1), Anneal-Bond furnace (C3), Al-Anneal furnace (C4), Oxidation 8" furnace (E1), Resist Pyrolysis furnace and RTP Annealsys.
Thermal oxidation can take place either by a dry process or by a wet process, depending on what furnace that is used for the oxidation. The film quality for a dry oxide is better than the film quality for a wet oxide with regards to density and dielectric constant. However, the oxidation rate is slowest for dry oxidation.
- Dry oxidation is used to grow 5 nm - 300 nm of silicon oxide. Dry oxidation can be done in the A1, A2, A3, C1, C3, C4, E1 and Resist Pyrolysis furnaces.
- Wet oxidation is used to grow up to ~3 µm of silicon oxide. Wet oxidation can be done in the A1, A3, C1, C3 and E1 furnaces.
Wafers with oxide layers thicker than ~3 µm can normally not be made in the cleanroom and will have to be bought from somewhere else (but check the wafer shop first - there might be some on stock). It is NOT allowed to oxidize the same wafers two times to get a thicker layer than 3 µm without approval.
Thermal oxidation can done at temperatures up to 1050 C - 1150 C, depending on the furnace - and especially the diameter of the quartz tube in the furnace. At these high temperatures, the quartz tube might start to deform, so therefore the oxidation times are restricted:
- A1, A2, A3, C3 and C4 furnaces: Maximum allowed oxidation time at 1150 C: 8 hours
- A1, A2, A3, C1, C3, C4 and E1 furnaces: Maximum allowed oxidation time at 1100 C: 23 hours (this will result in ~3 um wet oxide)
- Resist Pyrolysis furnace: Maximum allowed oxidation time at 1050 C: 3 hours
The standard recipes, quality control limits and results for the Boron Drive-in + Pre-dep furnace (A1) and the Phosphorus Drive-in furnace (A3) can be found here:
- Standard recipes, QC limits and results for the Boron Drive-in + Predep furnace (A1)
- Standard recipes, QC limits and results for the Phosphorus Drive-in furnace (A3)
The wet oxidation rates for the Anneal-Bond furnace (C1) can be found here:
Standard recipes in the oxidation furnaces
The steps in the standard oxidation recipes in the A-stack furnaces (A1, A2 and A3) and the C-stack furnaces (C1, C3 and C4) can be found here:
Comparison of the oxidation furnaces
| Generel description |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxidation method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Annealing gas |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Process temperature |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Substrate and batch size |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Allowed materials |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oxidation curves
Color chart for oxide/nitride thickness
Generic calculator for wet/dry oxide thickness calculation
The following links give an approximate oxide time/thickness based on a general formula:
Deal-Grove parameters
By Kasper Reck-Nielsen February 2015
The following table contains linear and parabolic parameters for use in the Deal-Grove model for thermal oxidation. The parameters are obtained a least squares fit to data available in the furnace logbooks. Information on wafer orientation and doping concentration, which is not available in the logbooks, has not been included in calculating the parameters.
| Anneal Oxide | Anneal Bond | Boron Drive-in | Gate Oxide | Phosphor Drive-in | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recipe | B [µm2/h] | B/A [µm/h] | RMSE [nm] | B [µm2/h] | B/A [µm/h] | RMSE [nm] | B [µm2/h] | B/A [µm/h] | RMSE [nm] | B [µm2/h] | B/A [µm/h] | RMSE [nm] | B [µm2/h] | B/A [µm/h] | RMSE [nm] |
| DRY900 | 0.000408 | 0.107 | Too little data | 0.0660 | 0.272 | 31 | 0.000390 | 0.154 | Too little data | 0.0028 | 0.079 | 4 (limited data) | 0.0507 | 0.884 | Too little data |
| DRY1000 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.465 | 0.838 | 20 | - | - | - | 0.641 | 1.45 | 41 |
| DRY1050 | 0.0111 | 0.526 | 27 | - | - | - | 0.0129 | 0.330 | 8 | 0.022 | 0.505 | 3 (limited data) | 0.0134 | 0.362 | 6 |
| DRY1100 | 0.020 | 0.930 | 10 | - | - | - | 0.0212 | 0.736 | 23 | - | - | - | 0.0313 | 0.553 | 14 |
| WET950 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.0716 | 1.25 | 12 | - | - | - | 0.110 | 1.17 | 11 | |
| WET1000 | 0.192 | 1.54 | 44 | - | - | 0.192 | 1.80 | 29 | - | - | - | 0.195 | 2.49 | 22 | |
| WET1050 | 0.487 | 0.965 | 29 | 0.477 | 0.899 | Too little data | 0.455 | 1.33 | 16 | - | - | - | 0.448 | 1.73 | 12 |
| WET1100 | 0.580 | 1.43 | 8 | - | - | - | 0.519 | 1.186 | 3 | - | - | - | 0.403 | 9.05 | 7 |
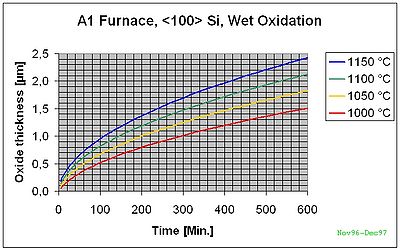
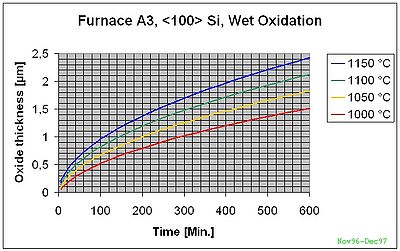
Wet Oxidation on <100>
The curves below are based on measurements in our specific furnaces and give more accurate results. We will still recommend to make minimum one test run if the thickness is very important.
- Wet oxidation
-
A1 Furnace <100>-Si Wet Oxidation
-
A3 Furnace <100>-Si Wet Oxidation
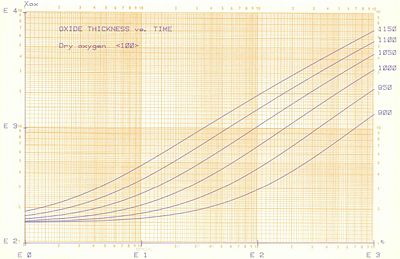
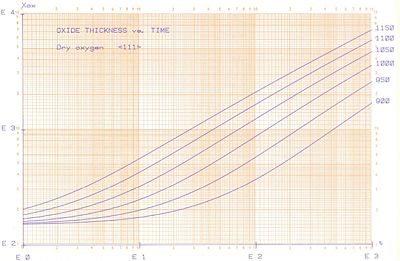
Dry Oxidation on <100> and <111> wafer
- Dry oxidation
-
Dry oxide on <100> wafer. The y-axis is in Å and the x-axis is in minutes.
-
Dry oxide on <111> wafer. The y-axis is in Å and the x-axis is in minutes.
Breakdown voltage measurements
In order to evaluate the quality of the oxide layers that can be grown in the oxidation furnaces, some breakdown voltage measurement have been made.
The results can be found on this page: