Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/EBLsubstratePrep: Difference between revisions
| (51 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
We recommend all groups or users to have their own bottle of e-beam resist inside the cleanroom. Please follow the [[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/ResistBottles|user resist bottles in the cleanroom guide.]] | We recommend all groups or users to have their own bottle of e-beam resist inside the cleanroom. Please follow the [[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/ResistBottles|user resist bottles in the cleanroom guide.]] | ||
==DTU Nanolab supplied EBL resists== | |||
| Line 19: | Line 21: | ||
|'''Technical reports''' | |'''Technical reports''' | ||
|'''Spin Coater''' | |'''Spin Coater''' | ||
|'''Thinner''' | |'''Thinner''' | ||
|'''Developer''' | |'''Developer''' | ||
| Line 35: | Line 36: | ||
|[https://www.allresist.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2020/03/AR-P6200_CSAR62english_Allresist_product-information.pdf AR-P 6200 info] | |[https://www.allresist.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2020/03/AR-P6200_CSAR62english_Allresist_product-information.pdf AR-P 6200 info] | ||
|[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/Coaters#Spin Coater: Gamma E-beam and UV|Spin Coater: Gamma E-beam and UV]] or [[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/Coaters#Manual_Spin_Coaters|Spin Coater: LabSpin 02/03]] | |[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/Coaters#Spin Coater: Gamma E-beam and UV|Spin Coater: Gamma E-beam and UV]] or [[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/Coaters#Manual_Spin_Coaters|Spin Coater: LabSpin 02/03]] | ||
|Anisole | |Anisole | ||
| | | | ||
ZED N50 | |||
|IPA | |IPA | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 55: | Line 52: | ||
|[https://www.allresist.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2020/03/SXAR-N8200-1_english_Allresist_product_information.pdf AR-N 8200 info] | |[https://www.allresist.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2020/03/SXAR-N8200-1_english_Allresist_product_information.pdf AR-N 8200 info] | ||
|[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/Coaters#Manual_Spin_Coaters|Spin Coater: LabSpin 02/03]] | |[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/Coaters#Manual_Spin_Coaters|Spin Coater: LabSpin 02/03]] | ||
|AR 600-07 | |AR 600-07 | ||
|AR 300-47:DIW (1:1) | |AR 300-47:DIW (1:1) | ||
| Line 63: | Line 59: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|-style="background: | |-style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black" | ||
|''' | |'''AR-N 7520''' | ||
|Negative | |Negative | ||
|[http://www.allresist.com AllResist] | |[http://www.allresist.com AllResist] | ||
|[ | |[[media:AR-N7500-7520.pdf|AR-N7500-7520]] | ||
|[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/Coaters#Manual_Spin_Coaters|Spin Coater: LabSpin 02/03]] | |[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/Coaters#Manual_Spin_Coaters|Spin Coater: LabSpin 02/03]] | ||
|PGMEA | |PGMEA | ||
| | | | ||
*AR 300-47 | *AR 300-47 | ||
* | *MIF 726 | ||
| | |H2O | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | |- | ||
|-style="background:LightGrey; color:black" | |||
|'''[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/AR-P 617|AR-P 617]]''' | |||
|Positive | |||
|[http://www.allresist.com AllResist] | |||
|[https://www.allresist.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2020/03/AR-P610_english_Allresist_product-information.pdf AR-P 617 info] | |||
|[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/Coaters#Manual_Spin_Coaters|Spin Coater: LabSpin 02/03]] | |||
|PGMEA | |||
|AR 600-50 | |||
|IPA | |||
|Remover 1165 | |||
| | |||
Resist | |- | ||
|-style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black" | |||
|'''[[Specific Process Knowledge/Lithography/EBeamLithography/ma-N 2400|ma-N 2400]]''' | |||
|Negative | |||
|[https://www.microresist.de/en/produkt/ma-n-2400-series/ Micro Resist Technology] | |||
| | |||
|[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/Coaters#Manual_Spin_Coaters|Spin Coater: LabSpin 02/03]] | |||
|Anisole | |||
| | |||
*MIF 726 | |||
*ma-D 525 | |||
|H2O | |||
|mr-Rem 700 | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
==User supplied resists== | |||
It is possible to obtain permission to user other resists at DTU Nanolab, users must however provide these resists and possibly developers themselves. A non-exhaustive list of user supplied EBL resist used at DTU Nanolab and some process guidelines can be found in the table below. | It is possible to obtain permission to user other resists at DTU Nanolab, users must however provide these resists and possibly developers themselves. A non-exhaustive list of user supplied EBL resist used at DTU Nanolab and some process guidelines can be found in the table below. | ||
| Line 170: | Line 189: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|-style="background:LightGrey; color:black" | |-style="background:LightGrey; color:black" | ||
|'''AR-N | |'''[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/ARN7500|AR-N 7500]]''' | ||
|Negative | |Negative | ||
|[http://www.allresist.com AllResist] | |[http://www.allresist.com AllResist] | ||
| | |[https://www.allresist.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2020/03/AR-N7500_english_Allresist_product-information.pdf AR-N 7500 info] | ||
|[[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Lithography/Coaters#Manual_Spin_Coaters|Spin Coater: LabSpin 02/03]] | |||
| | |a = 17126, b = -0.435 | ||
|PGMEA | |PGMEA | ||
| | | | ||
*AR 300-47:DIW (4:1) | |||
*MIF726:DIW (8:5) | |||
|DIW | |||
| | |||
*AR 300-73 | |||
*O2 plasma | |||
| | | | ||
| Line 215: | Line 238: | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
==Current EBL resist stock== | |||
The table below indicates the current stock of Nanolab provided EBL resists in the resist cupboard in E4. | |||
{|border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="3" style="text-align:left;" width=" | {|border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="3" style="text-align:left;" width="800px" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 231: | Line 255: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|-style="background:LightGrey; color:black" | |||
|AR-P 6200.09 | |||
| 1 L | |||
| 2026 | |||
| 1 | |||
|- | |- | ||
|-style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black" | |-style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black" | ||
|AR-P 6200.04 | |||
| 1 L | |||
| 2026 | |||
| 1 | |||
|- | |||
|-style="background:LightGrey; color:black" | |||
|AR-P 6200.04 | |||
| 0.25 L | |||
| 2019 | |||
| 0.25 | |||
|- | |||
|-style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black" | |||
|AR-P 6200.04 | |AR-P 6200.04 | ||
| | | 0.25 L | ||
| 2019 | |||
| 0.1 | |||
|- | |||
|-style="background:LightGrey; color:black" | |||
|AR-N 7520.07 New | |||
| 1 L | |||
| 2018 | |||
| 0.8 | |||
|- | |||
|-style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black" | |||
|AR-N 7520.11 New | |||
| 0.25 L | |||
| 2024 | |||
| 0.25 | |||
|- | |||
|-style="background:LightGrey; color:black" | |||
|AR-N 7520.17 New | |||
| 0.25 L | |||
| 2026 | | 2026 | ||
| | | 0.25 | ||
|- | |||
|-style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black" | |||
|AR-N 7520.18 | |||
| 1 L | |||
| 2016 | |||
| 0.7 | |||
|- | |||
|-style="background:LightGrey; color:black" | |||
|AR-N 8200.06 | |||
| 0.1 L | |||
| 2021 | |||
| 0.1 | |||
|- | |||
|-style="background:WhiteSmoke; color:black" | |||
|AR-N 8200.03 | |||
| 0.25 L | |||
| 2023 | |||
| 0.25 | |||
|} | |} | ||
=== Discharge layer application | <br clear="all" /> | ||
== Discharge layer application == | |||
As exposure is done with an electron beam, insulating substrates will cause a build up of charge that will deflect the incoming beam and disturb pattern definition. It is therefore necesarry when working with insulating substrates or substrates with thick (> 200 nm) dielectric films to apply a discharge layer. This is typically applied on top of the EBL resist layer and must be removed in between exposure and development. The most common discharge layer is 20 nm thermally evaporated Al. Bear in mind that it should be thermally evaporated and not e-beam evaporated. Thermal evaporation of Al can be done in [[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Thin film deposition/thermalevaporator|Thermal evaporator]] and [[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Thin film deposition/Wordentec|Wordentec]]. The Al layer can be removed with MIF726 after exposure. MIF726 etch rate in Al is about 0.5 nm/s, although only about 1 nm/min in oxidized aluminium. | As exposure is done with an electron beam, insulating substrates will cause a build up of charge that will deflect the incoming beam and disturb pattern definition. It is therefore necesarry when working with insulating substrates or substrates with thick (> 200 nm) dielectric films to apply a discharge layer. This is typically applied on top of the EBL resist layer and must be removed in between exposure and development. The most common discharge layer is 20 nm thermally evaporated Al. Bear in mind that it should be thermally evaporated and not e-beam evaporated. Thermal evaporation of Al can be done in [[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Thin film deposition/thermalevaporator|Thermal evaporator]] and [[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Thin film deposition/Wordentec|Wordentec]]. The Al layer can be removed with MIF726 after exposure. MIF726 etch rate in Al is about 0.5 nm/s, although only about 1 nm/min in oxidized aluminium. | ||
For samples with 2D materials such as graphene, HBN, etc., it is '''mandatory''' to apply a 20 nm Al layer on top of the resist in order to expose the substrate in the JEOL 9500 system. The Raith eLine system does not have this requirement. | For samples with 2D materials such as graphene, HBN, etc., it is '''mandatory''' to apply a 20 nm Al layer on top of the resist in order to expose the substrate in the JEOL 9500 system. The Raith eLine system does not have this requirement. | ||
== Inspection == | |||
Post exposure pattern dimensions are dependent on resist thickness. Thus, it is advisable to verify resist thickness after spin coating. This can be done by ellipsometry in the [[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Characterization/Optical_characterization#Ellipsometer|VASE Ellipsometer]]. | Post exposure pattern dimensions are dependent on resist thickness. Thus, it is advisable to verify resist thickness after spin coating. This can be done by ellipsometry in the [[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Characterization/Optical_characterization#Ellipsometer|VASE Ellipsometer]]. | ||
Latest revision as of 10:49, 31 May 2024
Resist coating
An appropriate EBL resist must naturally be applied to the substrate. DTU Nanolab supplies a number of standard resists, please consult the table below. The default positive EBL resist is AR-P 6200.09 (CSAR). CSAR is installed on Spin Coater: Gamma E-beam and UV for spin coating of 2", 4" and 6" substrates. For other substrate sizes (i.e. chips) or other resists Spin Coater: LabSpin 02/03 have to be used instead. The standard resist bottles are stored in the chemical cupboard in E-4.
We recommend all groups or users to have their own bottle of e-beam resist inside the cleanroom. Please follow the user resist bottles in the cleanroom guide.
DTU Nanolab supplied EBL resists
| DTU Nanolab supplied standard EBL resists and process guides | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resist | Polarity | Manufacturer | Technical reports | Spin Coater | Thinner | Developer | Rinse | Remover | Process flows (in docx-format) | |
| CSAR AR-P 6200 | Positive | AllResist | AR-P 6200 info | Spin Coater: Gamma E-beam and UV or Spin Coater: LabSpin 02/03 | Anisole |
ZED N50 |
IPA |
|
CSAR CSAR with Al LOR5A with CSAR | |
| Medusa AR-N 8200 | Negative | AllResist | AR-N 8200 info | Spin Coater: LabSpin 02/03 | AR 600-07 | AR 300-47:DIW (1:1) | DIW | BOE | ||
| AR-N 7520 | Negative | AllResist | AR-N7500-7520 | Spin Coater: LabSpin 02/03 | PGMEA |
|
H2O | |||
| AR-P 617 | Positive | AllResist | AR-P 617 info | Spin Coater: LabSpin 02/03 | PGMEA | AR 600-50 | IPA | Remover 1165 | ||
| ma-N 2400 | Negative | Micro Resist Technology | Spin Coater: LabSpin 02/03 | Anisole |
|
H2O | mr-Rem 700 | |||
User supplied resists
It is possible to obtain permission to user other resists at DTU Nanolab, users must however provide these resists and possibly developers themselves. A non-exhaustive list of user supplied EBL resist used at DTU Nanolab and some process guidelines can be found in the table below.
| Non standard, user supplied EBL resists and process guides | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resist | Polarity | Manufacturer | Comments | Technical reports | Spin Coater | Thinner | Developer | Rinse | Remover | Process flows (in docx-format) |
| ZEP520A | Positive resist, contact Lithography if you plan to use this resist | ZEON | Positive resist | ZEP520A.pdf, ZEP520A spin curves on SSE Spinner | See table here | Anisole | ZED-N50/Hexyl Acetate,n-amyl acetate, oxylene. JJAP-51-06FC05, JVB001037 | IPA | acetone/1165 | Process Flow ZEP
|
| Copolymer AR-P 617 | Positive | AllResist | Approved, not tested yet. Used for trilayer (PE-free) resist-stack or double-layer lift-off resist stack. Please contact Lithography for information. | AR_P617 | See table here | PGME | AR 600-55, MIBK:IPA | acetone/1165 | Trilayer stack: Process Flow | |
| mr EBL 6000.1 | Negative | MicroResist | Standard negative resist | mrEBL6000 processing Guidelines | See table here | Anisole | mr DEV | IPA | mr REM | Process Flow |
| HSQ (XR-1541) | Negative | DOW Corning | Approved. Standard negative resist | HSQ Dow Corning, MSDS HSQ | See table here | TMAH, AZ400K:H2O | H2O | process flow HSQ | ||
| AR-N 7500 | Negative | AllResist | AR-N 7500 info | Spin Coater: LabSpin 02/03 | a = 17126, b = -0.435 | PGMEA |
|
DIW |
|
|
| PMMA | Positive | AllResist | See table here | Anisole | MIBK:IPA (1:3), IPA:H2O | IPA | acetone/1165/Pirahna |
| ||
| ZEP7000 | Positive | ZEON | Not approved. Low dose to clear, can be used for trilayer (PEC-free) resist-stack. Please contact Lithography for information. | ZEP7000.pdf | See table here | Anisole | ZED-500/Hexyl Acetate,n-amyl acetate, oxylene. | IPA | acetone/1165 | Trilayer stack: Process Flow |
Current EBL resist stock
The table below indicates the current stock of Nanolab provided EBL resists in the resist cupboard in E4.
| Current EBL resist stock in E4 (updated 2023-09-04) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Resist | Bottle size | Expiration | Approximate amount remaining [L] |
| AR-P 6200.09 | 1 L | 2026 | 1 |
| AR-P 6200.04 | 1 L | 2026 | 1 |
| AR-P 6200.04 | 0.25 L | 2019 | 0.25 |
| AR-P 6200.04 | 0.25 L | 2019 | 0.1 |
| AR-N 7520.07 New | 1 L | 2018 | 0.8 |
| AR-N 7520.11 New | 0.25 L | 2024 | 0.25 |
| AR-N 7520.17 New | 0.25 L | 2026 | 0.25 |
| AR-N 7520.18 | 1 L | 2016 | 0.7 |
| AR-N 8200.06 | 0.1 L | 2021 | 0.1 |
| AR-N 8200.03 | 0.25 L | 2023 | 0.25 |
Discharge layer application
As exposure is done with an electron beam, insulating substrates will cause a build up of charge that will deflect the incoming beam and disturb pattern definition. It is therefore necesarry when working with insulating substrates or substrates with thick (> 200 nm) dielectric films to apply a discharge layer. This is typically applied on top of the EBL resist layer and must be removed in between exposure and development. The most common discharge layer is 20 nm thermally evaporated Al. Bear in mind that it should be thermally evaporated and not e-beam evaporated. Thermal evaporation of Al can be done in Thermal evaporator and Wordentec. The Al layer can be removed with MIF726 after exposure. MIF726 etch rate in Al is about 0.5 nm/s, although only about 1 nm/min in oxidized aluminium.
For samples with 2D materials such as graphene, HBN, etc., it is mandatory to apply a 20 nm Al layer on top of the resist in order to expose the substrate in the JEOL 9500 system. The Raith eLine system does not have this requirement.
Inspection
Post exposure pattern dimensions are dependent on resist thickness. Thus, it is advisable to verify resist thickness after spin coating. This can be done by ellipsometry in the VASE Ellipsometer.
As the cleanliness requirement of the JEOL is very high, substrates that does not visually appear to be in a good condition will be rejected by the JEOL 9500 cassette loading team. It is therefore a good idea to perform your own visual inspection. The loading team will inspect your samples for any types of flakes or bubbles in the surface layers of the sample. Samples with flakes or bubbles will be rejected.
Samples with resist residues on the backside will also be rejected. If you have resist residues on the backside of your wafer you should wipe it off with an appropriate solvent.
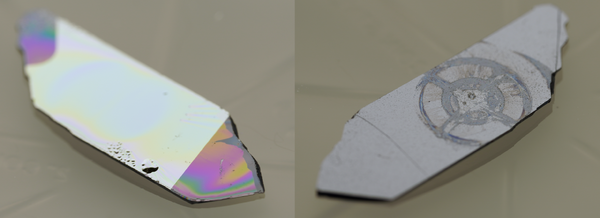
|
|
Example of rejected samples with visible bubbles in resist/Al coating and (a lot) of resist residue on the backside. Photo: Thomas Pedersen. |
