Specific Process Knowledge/Etch/DRIE-Pegasus/picoscope: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 119: | Line 119: | ||
* The shorter cycle times (Process A has 11 seconds full cycle and Process D4 has 3.2 second full cycle) emphasize the need for the faster process parameter sampling rate. For instance, a dep cycle with one measurement point for the C<sub>4</sub>F<sub>8</sub> flow is no good. | * The shorter cycle times (Process A has 11 seconds full cycle and Process D4 has 3.2 second full cycle) emphasize the need for the faster process parameter sampling rate. For instance, a dep cycle with one measurement point for the C<sub>4</sub>F<sub>8</sub> flow is no good. | ||
* The oscillations in pressure now last the entire dep cycle - it never stabilizes. | * The oscillations in pressure now last the entire dep cycle - it never stabilizes. | ||
* Optimizing a recipe to arrive at a minimum reflected power, for both coil and platen, using the Pro software datalogging may be somewhat illusory as it only picks a fraction of the spikes occurring at every change of plasma conditions. | * Optimizing a recipe to arrive at a minimum reflected power, for both coil and platen, using the Pro software datalogging may be somewhat illusory as it only picks up a fraction of the spikes occurring at every change of plasma conditions. | ||
What to do about this? | What to do about this? | ||
| Line 128: | Line 128: | ||
Changing the pressure in the plasma has a great impact on the RF matching conditions as illustrated for [[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Etch/DRIE-Pegasus/System-description#Why_RF_matching_is_extremely_important_in_the_Bosch_process | an oxygen plasma]] elsewhere. The obvious place to start is therefore the pressure. Also, it barely makes sense to claim that the pressure is 20 mtorr in the dep phase if it oscillates as shown for the Process D4 above. | Changing the pressure in the plasma has a great impact on the RF matching conditions as illustrated for [[Specific_Process_Knowledge/Etch/DRIE-Pegasus/System-description#Why_RF_matching_is_extremely_important_in_the_Bosch_process | an oxygen plasma]] elsewhere. The obvious place to start is therefore the pressure. Also, it barely makes sense to claim that the pressure is 20 mtorr in the dep phase if it oscillates as shown for the Process D4 above. | ||
Compared to many other vacuum systems the pegasus tools require a massive turbo pump | |||
With a huge turbo pump | |||
The pressure in the process chamber is regulated by the throttle valve or APC (Automatic Pressure Valve) that sits in front of the turbo pump. With a large valve plate sitting across the opening between the process chamber and turbo pump, this valve is capable of changing the pumping speed of the system. | |||
By precisely changing this opening, it can | |||
It changes the opening | |||
capable of opening and closing very precisely and very quickly. If it | |||
If a process is running at some | |||
The oscillations are caused by the fact that we use the 'fixed pressure' mode. | The oscillations are caused by the fact that we use the 'fixed pressure' mode. | ||
Revision as of 13:48, 18 March 2020
Feedback to this page: click here
Process optimization using the Picoscope
Before going into details on why it makes sense to optimize the processes using the picoscope process monitoring, we need to have a look at how monitoring processes is usually done.
Standard process parameter monitoring
The original standard recipes on Pegasus 1 differ in many ways. Here, we go through two of them.
Process A
The process parameters of the second step of Process A is listed in the table below:
| Process A Step 2 parameters | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Etch | Dep |
| Gas flow (sccm) | SF6 350 (1.5 s), 550 | C4F8 200 |
| Cycle time (secs) | 7.0 | 4.0 |
| Pressure (mtorr) | 25 (1.5 s), 150 | 25 |
| Coil power (W) | 2800 | 2000 |
| Platen power (W) | 140 (1.5) 45 | 0 |
| Common | Temperature 20 degs | |
When running any recipe on the SPTS Pro software, a set of process parameters are recorded as the process runs. This data can be accessed later by looking up the datalog. Which parameters are recorded is dictated by the so-called logging recipe that is selected for every process recipe. The list of possible parameters to include in a logging recipe is long and is comprised of both input parameters such as 'Coil forward power demand' and 'SF6 flow setpoint', and measured values such as 'Platen temperature' and 'Platen DC Bias'. During the process itself, one can also activate the 'Trace' to monitor the process parameters in real time.
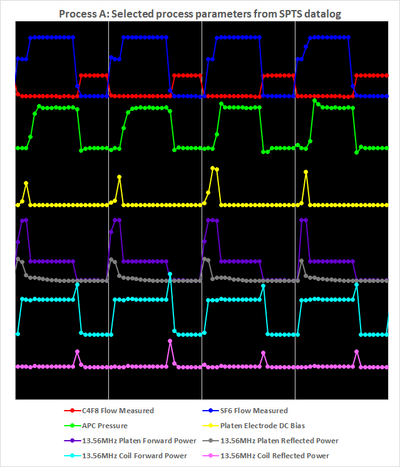
To the left in the figure below, some of the most important process parameters are shown for a process run of the recipe Process A.
- 4 cycles of Process A
-
Left: Recorded with the SPTS software
-
Right: Recorded with the Picoscope
Above to the left, one can see the multiplexing of the Bosch process by alternation of the gas flows of SF6 (that has flow initially at 350 sccm in the break for the first 1.5 second then 550 sccm for 5.5 seconds in the main etch phase) and C4F8 (at 200 sccm in the dep phase) according to the process recipe table above. Below, the Pressure alternates between 25 mtorr (dep and break) and 150 mtorr (main). The Platen Electrode DC Bias (the electrostatic potential difference between the plasma and the wafer electrode that drives the ion bombardment in the etch process) is generated by the Platen Power at 140 W in the break and 45 W in the main etch. Below this, the Reflected Platen Power is not zero. The Coil Power is 2800 W (etch) and 2000W (dep) with the Reflected Coil Power below. The spikes in Coil Power at every point where the Reflected is not zero indicates that the Coil Power is running in Load mode (as opposed to Forward mode) where the power lost as reflected power is compensated for by increasing the input power.
Process A has 4 second dep phase and 7 second (1.5 second break and 5.5 second main) and the SPTS Pro software samples the process parameters every 0.5 second. This produces plots as seen above where all measurements have markers. One can ask the questions:
- What happens if the cycle duration is lowered in order produce smaller scallops?
- How do we know if something that is very brief happens? For instance, spikes in reflected power can be rather short lived as indicated by the one point spikes of reflected coil power above.
In both cases, the sampling frequency of 2 Hz is simply not high enough - we need to increase this. The SPTS Pro software can only lower this. However, realizing that all the devices (mass flow controllers, pressure gauges, RF generators etc.) responsible for the parameters in the plot above are produce output measurements in real time, we can sample these parameters by some external device. Enter the Picoscope oscilloscope with 8 analog channels that enable us sample up to 8 outputs, usually a DC voltage, at almost any sampling rate. Unlike the old oscilloscopes, the Picoscope is fully operated by a software that produces a vast amount of data and nice plots. We therefore have to decide which process parameters are the most important to monitor and then go through the electrical diagrams to find an appropriate place to pick up the signal. This set of parameters is chosen as shown in the plots above.
Comparing the two plots we observe the following:
- There is, indeed, short lived incidences that are not picked up by the SPTS Pro software:
- Spikes of high flow when the C4F8 MFC opens.
- Spikes of reflected coil power.
- The reading of the DC Bias has much more detail than the one-point reading of the Pro software indicates.
- There are oscillations in the pressure every time whenever there is a change of gas flow
Since Process A is a standard recipe we will not change it as it is. Before deciding what to do we'll have a look at another recipe with shorter cycles.
Process D4
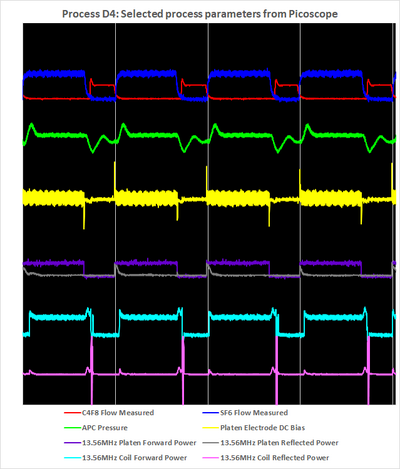
After a few years in its original configuration, we decided to upgrade Pegasus 1 with the High flow plenum upgrade to improve the fast switching performance. As a result, the original recipe Process D was changed to Process D4 with faster cycles. The process parameters are listed in the table below.
| Process D4 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Etch | Dep |
| Gas flow (sccm) | SF6 275, O2 | C4F8 150 |
| Cycle time (secs) | 2.2 | 1 |
| Pressure (mtorr) | 26 | 20 |
| Coil power (W) | 2500 | 2000 |
| Platen power (W) | 35 | 0 |
| Common | Temperature 0 degs | |
Running Process D4 while monitoring with the Pro software and Picoscope produces plots as shown below.
- 4 cycles of Process D4
-
Left: Recorded with the SPTS software
-
Right: Recorded with the Picoscope
Comparing to Process A we observe several things:
- The shorter cycle times (Process A has 11 seconds full cycle and Process D4 has 3.2 second full cycle) emphasize the need for the faster process parameter sampling rate. For instance, a dep cycle with one measurement point for the C4F8 flow is no good.
- The oscillations in pressure now last the entire dep cycle - it never stabilizes.
- Optimizing a recipe to arrive at a minimum reflected power, for both coil and platen, using the Pro software datalogging may be somewhat illusory as it only picks up a fraction of the spikes occurring at every change of plasma conditions.
What to do about this?
How to improve this
Minimizing the reflected power is essential to ensure that the instrument hardware doesn't degrade over time and that the users have accurate information about the processes. Realizing that there may be a challenge with detecting reflected powers we need to decide what to do. We can abandon all processes and start developing new ones - this will halt all processing. Instead, a set of new recipes will be developed.
Stabilizing the pressure
Changing the pressure in the plasma has a great impact on the RF matching conditions as illustrated for an oxygen plasma elsewhere. The obvious place to start is therefore the pressure. Also, it barely makes sense to claim that the pressure is 20 mtorr in the dep phase if it oscillates as shown for the Process D4 above.
Compared to many other vacuum systems the pegasus tools require a massive turbo pump With a huge turbo pump The pressure in the process chamber is regulated by the throttle valve or APC (Automatic Pressure Valve) that sits in front of the turbo pump. With a large valve plate sitting across the opening between the process chamber and turbo pump, this valve is capable of changing the pumping speed of the system.
By precisely changing this opening, it can It changes the opening
capable of opening and closing very precisely and very quickly. If it
If a process is running at some
The oscillations are caused by the fact that we use the 'fixed pressure' mode.