LabAdviser/314/Microscopy 314-307/SEM/Nova/Micro 4-point probe: Difference between revisions
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
= Micro 4-point probe = | = Micro 4-point probe = | ||
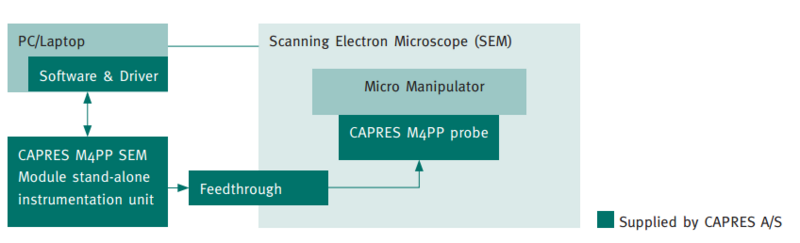
The electrical resistivity of metallic bulk and thin-film samples is usually measured by the 4-point probe technique. The classic arrangement, visible in Fig. | The electrical resistivity of metallic bulk and thin-film samples is usually measured by the 4-point probe technique. The classic arrangement, visible in Fig. 5, consists of four needle-like electrodes in a linear arrangement, with a current injected into the material via the outer two electrodes, while the resulting difference in electric potential is measured via the two inner electrodes. | ||
By using separate electrodes for the current injection and for the determination of the electric potential, the contact resistance between the metal electrodes and the material does not show up in the measured results. Since the contact resistance can be large and can strongly depend on the condition and materials of the electrodes, it is easier to interpret the data measured by the 4-point probe technique than from a 2-point probe system. If the sample has a | By using separate electrodes for the current injection and for the determination of the electric potential, the contact resistance between the metal electrodes and the material does not show up in the measured results. Since the contact resistance can be large and can strongly depend on the condition and materials of the electrodes, it is easier to interpret the data measured by the 4-point probe technique than from a 2-point probe system. If the sample has a finite size and if the spacing between the probes is | ||
s1= s2 = s3 = s, the resistivity is given by: | s1= s2 = s3 = s, the resistivity is given by: | ||
Revision as of 10:53, 9 July 2018
Kleindiek micromanipulator
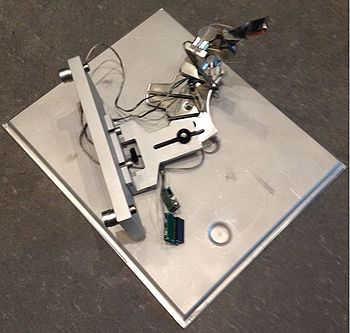
The Kleindiek Nanotechnik MM3A-EM is a plug and play micromanipulator for SEM/FIB applications, with a versatile range of modular plug-ins. The MM3A-EM can be used in most SEM/FIB instruments and offers fast setup and removal. The system consists of a base over which the micromanipulator arm is mounted (Figure 1). The base can be attached to the SEM front door by two exagonal head screws (Figure 2).The arm is connected to the external power supply through two plug-ins on a PCB board mounted on the SEM door.