Specific Process Knowledge/Etch/Etching of Silicon Oxide/SiO2 etch using AOE/Standard recipe with resist mask/Striation: Difference between revisions
< Specific Process Knowledge | Etch | Etching of Silicon Oxide | SiO2 etch using AOE | Standard recipe with resist mask
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
=Striation: Side wall roughness= | =Striation: Side wall roughness= | ||
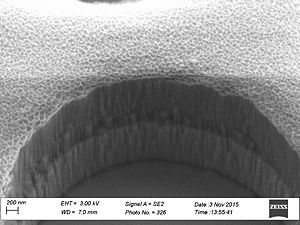
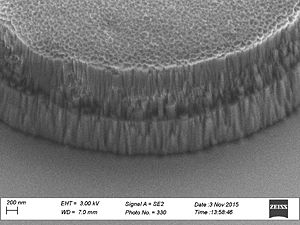
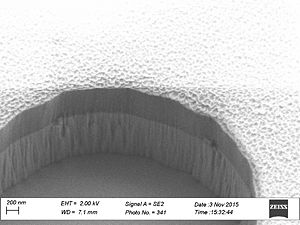
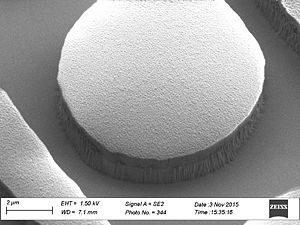
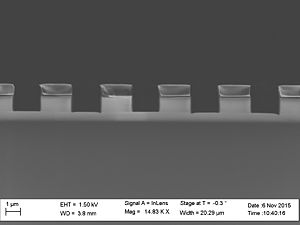
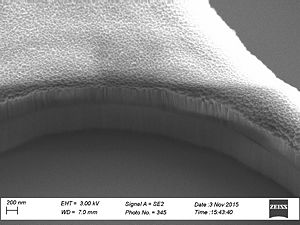
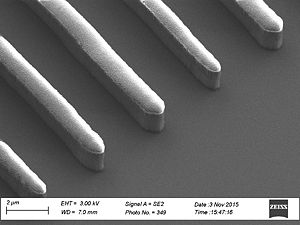
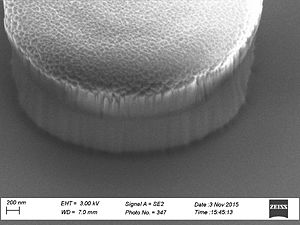
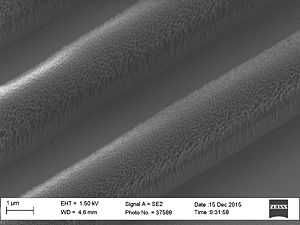
When etching silicon oxide rough sidewalls are most often seem. This effect is called striation, because it creates stripes along the etched profile. The litterature gives several coarses for this. The two main courses seems to be: # deposition on the sidewalls as the etch proceeds, coursing masking effects | When etching silicon oxide rough sidewalls are most often seem. This effect is called striation, because it creates stripes along the etched profile. The litterature gives several coarses for this. The two main courses seems to be: | ||
# deposition on the sidewalls as the etch proceeds, coursing masking effects | |||
# damage of the resist mask coursed by plasma heating and/or interaction with the resist. | # damage of the resist mask coursed by plasma heating and/or interaction with the resist. | ||
Revision as of 08:46, 20 April 2016
Feedback to this page: click here
Striation: Side wall roughness
When etching silicon oxide rough sidewalls are most often seem. This effect is called striation, because it creates stripes along the etched profile. The litterature gives several coarses for this. The two main courses seems to be:
- deposition on the sidewalls as the etch proceeds, coursing masking effects
- damage of the resist mask coursed by plasma heating and/or interaction with the resist.
This can be caused by polymer deposition which is a product of the process gasses. It can also be due to damage of the resist profile created during the etch this damage makes the resist edge rough and this pattern is transferred to the oxide profile. This effect is called striation, because it creates stripes along the etched profile. To avoid the polymer deposition one can chose to etch with
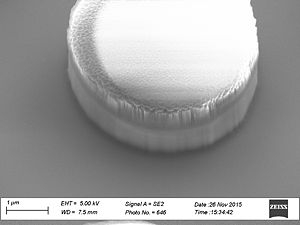
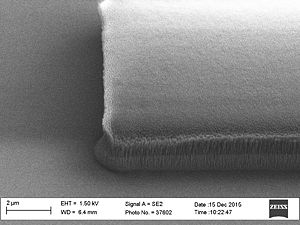
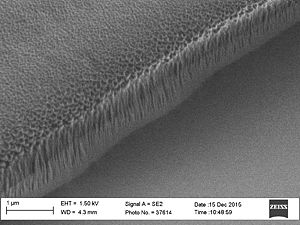
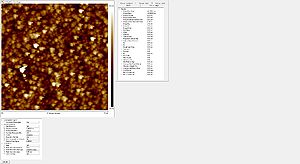
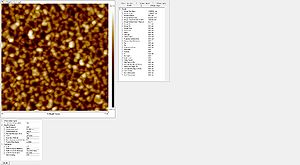
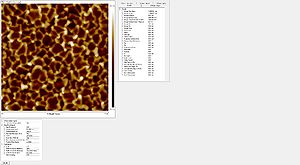
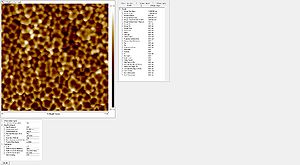
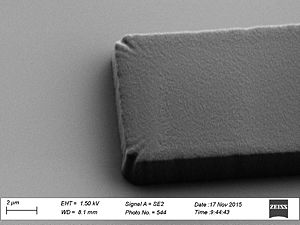
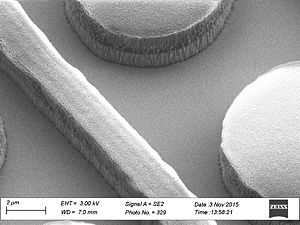
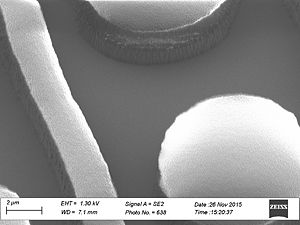
Sidewall roughness and resist surface after etch viewed with SEM
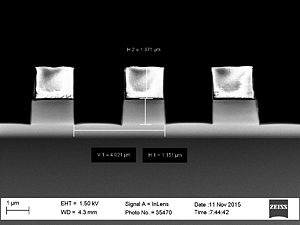
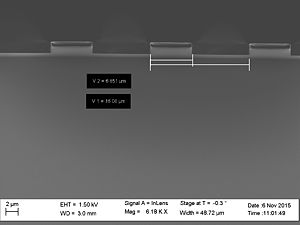
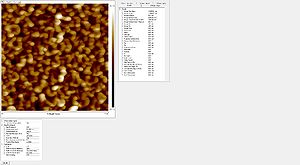
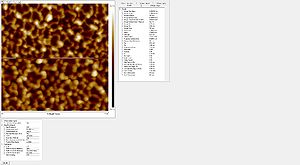
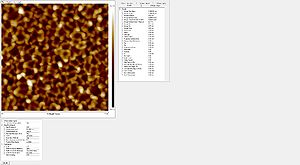
- Striation with different resists used
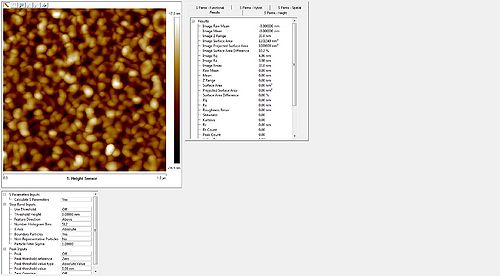
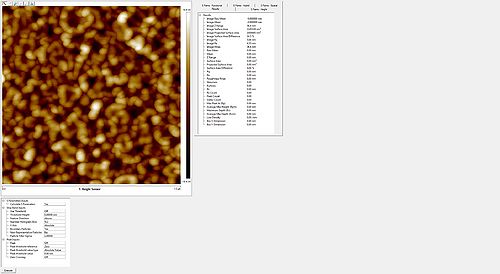
Roughness of the resist after etch measured with the AFM